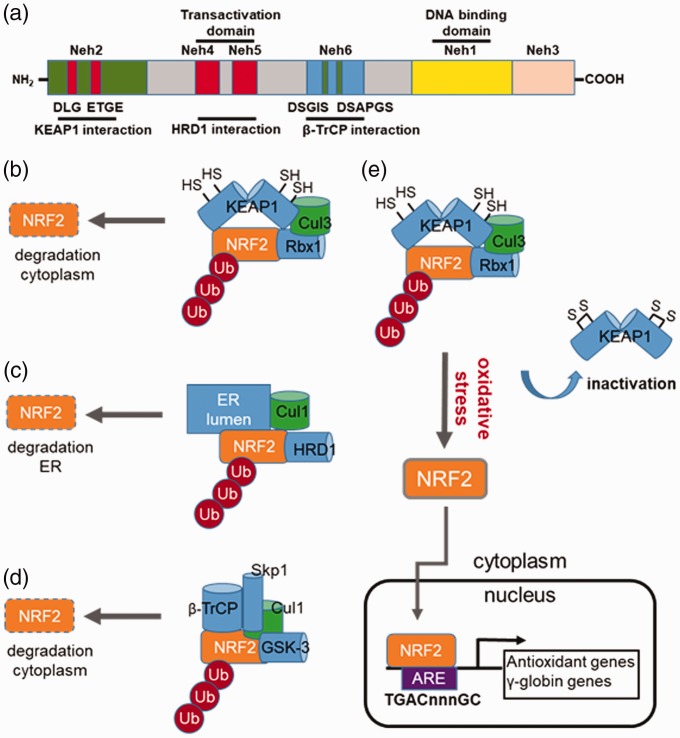
Figure 2.
Regulation of NRF2 stability by different E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes. (a) Shown is a schematic structure of the NRF2 protein domains such as Neh1 involved in small MAF heterodimerization and the transactivation domains Neh4 and Neh5 for interacting the co-activators CBP/p300. Also depicted are the individual domains in NRF2 required for interaction with KEAP1, HRD1, and β-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP). (b) KEAP1-mediated NRF2 repression. Under basal conditions, NRF2 activity is repressed through ubiquitination (Ub) via cullin-dependant E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul3, bound to Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1 (KEAP1). Multiple cysteines residues in KEAP1 including C151, C273 and C288 are required for its interaction with the DLG and ETGE motifs in the Neh2 domain of NRF2. When cysteine residues are modified by electrophiles or ROS, the conformation structure of KEAP1 is altered and interactions with NRF2 disrupted; the net result is reversal of NRF2 proteasomal degradation. (c) HRD1-mediated NRF2 repression. HRD1 is the E3 ubiquitin ligase, which resides in the ER. HRD1 ubiquitylates NRF2 after interacted with the Neh4 and Neh5 domains. (d) β-TrCP-mediate NRF2 repression. Shown is a schematic of NRF2 repression by β-TrCP, which interacts in the Neh6 domain of NRF2 comprising DSGIS and DSAPGS. The DSGIS motif contains a functional GSK-3 phosphorylation site that mediates NRF2 degradation. (e) Mechanism of KEAP1 inactivation that induce γ-globin gene expression. Several cysteine residues in KEAP1 are critical for interaction with NRF2; once modified through various mechanisms, disruption of interaction between KEAP1 and NRF2 occurs, which inhibits polyubiquitination of NRF2. Stabilized NRF2 undergoes nuclear translocation to activate target genes containing the antioxidant response element (ARE) including the antioxidant and γ-globin genes among others. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)