Figure 7.
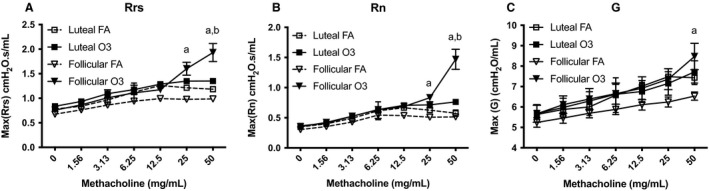
Effects of ozone exposure on lung mechanical properties in female mice at different phases of the estrous cycle. (A) Respiratory system resistance (Rrs). (B) Newtonian resistance (Rn). (C) Tissue damping (G). Respiratory function parameters were measured with a flexiVent system in female mice at 24 h after exposure to ozone (solid line) or filtered air (dashed line) in the follicular (inverted triangle) or luteal (square) phase of the estrous cycle. Exposure to ozone significantly increased Rrs and Rn at higher doses of methacholine in mice the follicular phase but not the luteal phase. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of data from 4 to 6 mice per group. FA, filtered air; O3, ozone; asignificantly different than luteal FA (P < 0.05), bsignificantly different than luteal O3 (P < 0.05).
