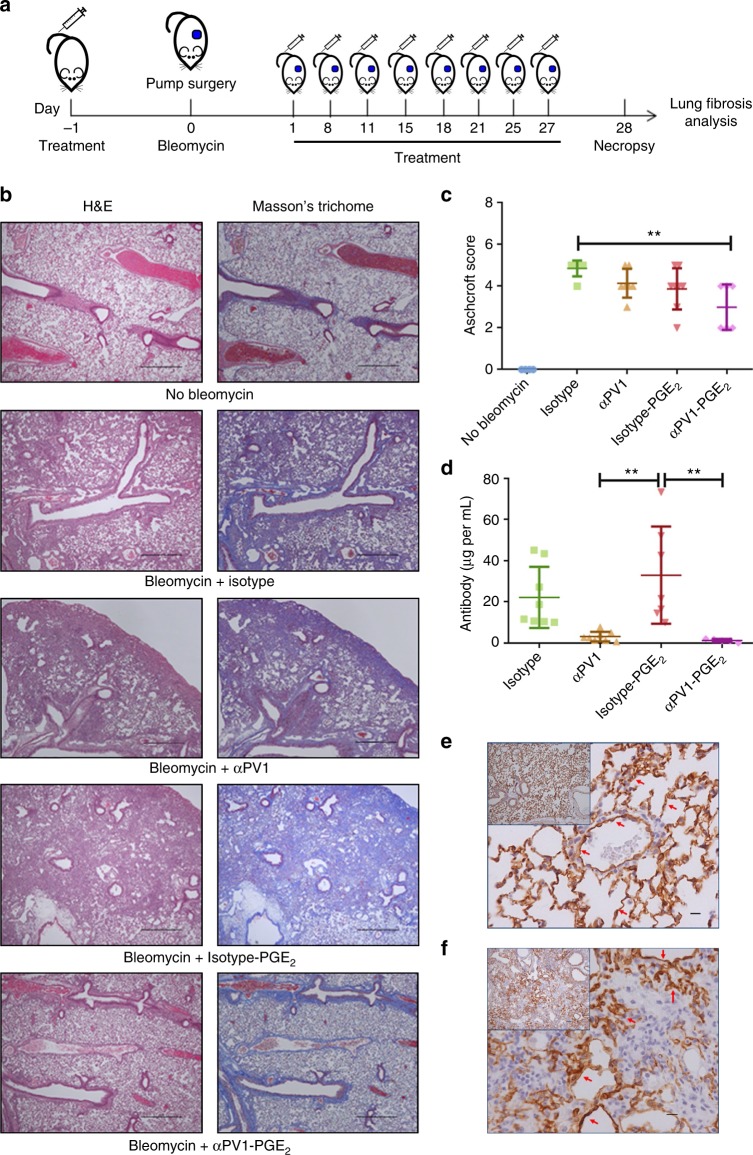
Fig. 4.
Anti-fibrotic activity of αPV1-PGE2 in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Schematic view of administration protocol (a). Representative images of lungs from mice from each treatment group are shown stained with H&E, and Masson’s Trichrome to highlight fibrosis (blue). The abundant extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition in the lungs from bleomycin isotype groups was substantially reduced in the lungs of animals treated with αPV1-PGE2; scale bars: 100 μm. Lung histological alterations were scored using a modified Ashcroft scale system. Reduction in the levels of lung fibrosis was observed for αPV1-PGE2-treated animals (c). Rapid reduction in serum antibody levels for the αPV1 groups was observed which is consistent with fast lung and kidney accumulation (d). αPV1 immunohistochemistry of lungs from control mice (e) and mice receiving bleomycin (f) illustrate PV1 expression remains high even in fibrotic lung tissue. Data represent mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA (Tukey post-hoc analyses) was used to evaluate the statistical significance (defined as a p-value < 0.05). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; scale bars = 10 μm; n = 8