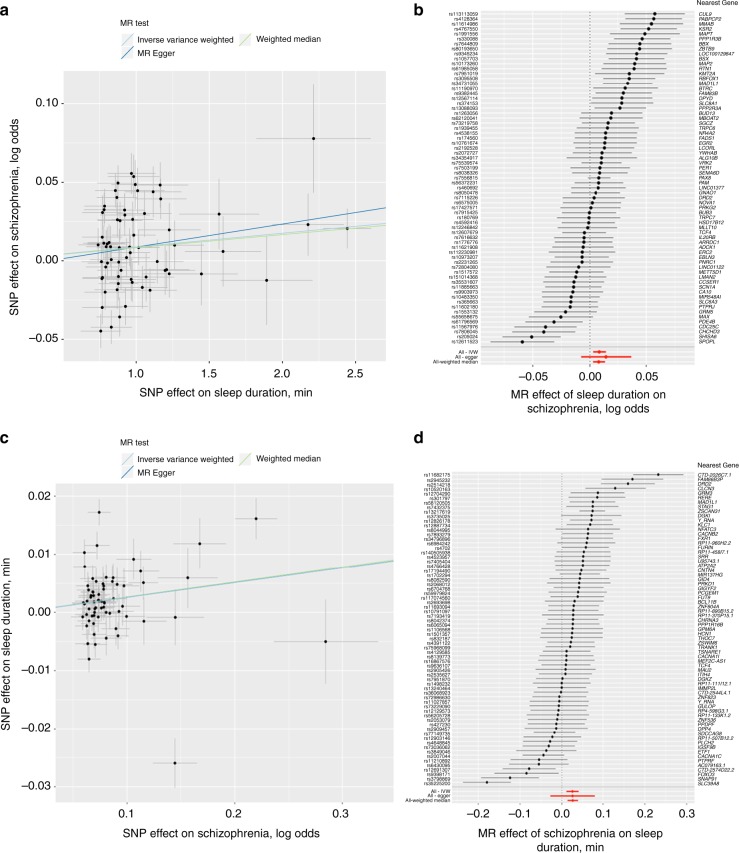
Fig. 4.
Bidirectional causal relationship of sleep duration with schizophrenia using Mendelian randomization. Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with sleep duration and schizophrenia (a) or SNP associated with schizophrenia and sleep duration (c) and forest plots show the estimate of the effect of genetically increased sleep duration on schizophrenia (b) or increased risk of schizophrenia on sleep duration (d). Lines identify the slopes for three Mendelian randomization (MR) association tests (a, c). Forest plots show each SNP with the 95% confidence interval (gray line segment; error bars) of the estimate and the inverse variance weighted, MR-Egger, and weighted median MR results in red