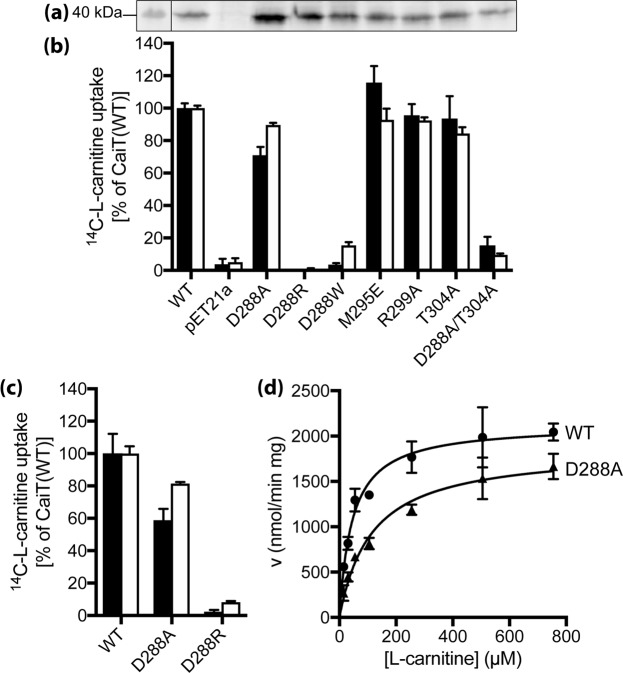
Figure 6.
Functional significance of trimeric contacts in CaiT. (a) Western blot analysis of CaiT with given amino acid replacements in E. coli JW0039 membranes. HRP-linked mouse anti-His IgG was used to detect CaiT. PageRuler Prestained Protein Ladder was used for molecular size estimation. Shown is the section of the blot that contains the CaiT band. The complete gel is presented in Fig. S6. (b) Initial rates of counterflow (black) and maximum accumulation of carnitine in E. coli JW0039 (white) were determined as described in the legend of Fig. 3. As negative control, cells carrying pET21a (nc) were used. (c) Initial rates of counterflow (black) and maximum accumulation (white) of carnitine catalyzed by CaiT variants in proteoliposomes. CaiT was purified and reconstituted as described1. The lipid to protein ratio of the resulting proteoliposomes was 100:1 (w/w). Proteoliposomes were preloaded with 10 mM unlabeled L-carnitine overnight. Aliquots of the proteoliposome suspension (1–2 µg of protein) were then diluted into 400 µL buffer containing 4.5 µM L-[methyl-14C]carnitine (55 Ci/mol) resulting in a final carnitine concentration of 54.5 µM. As negative control, proteoliposomes not preloaded with unlabeled carnitine (nc) were used and the obtained transport rates were used for correcting the data. Carnitine counterflow with cells or proteoliposomes was assayed at 25 °C under aerobic conditions using a rapid filtration method as described1. (d) Michaelis-Menten kinetics of L-carnitine counterflow in proteoliposomes reconstituted with wild-type CaiT (WT) or CaiT-D288A. Initial rates of L-[methyl-14C]carnitine uptake were measured at given substrate concentrations and plotted using the kinetic module of GraphPad Prism. For all experiments, standard deviations were calculated from triplicate determinations of a representative experiment.