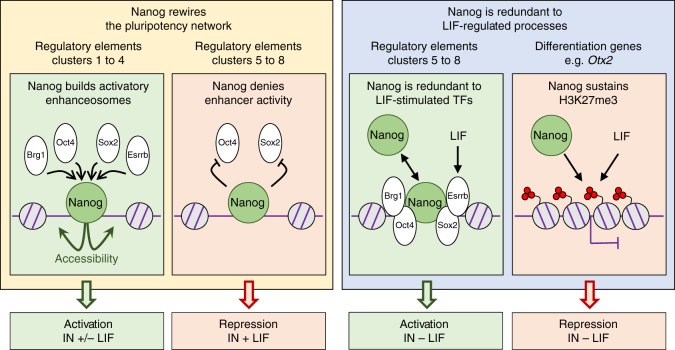
Fig. 6.
Nanog is a versatile TF impacting the pluripotency network and epigenome. The function of Nanog at stereotypical clusters of regulatory elements targeted by the pluripotency network, as well as at differentiation genes, is shown. Briefly, Nanog displays four major behaviours (left to right): 1/ recruitment of other factors (Oct4, Sox2 and Esrrb, together with Brg1) to promote chromatin accessibility and activate gene transcription; 2/ inhibiting enhancer activity, leading to gene repression either by blocking Oct4/Sox2 recruitment (shown) or by other mechanisms (not shown for simplicity; see text for details); 3/ complementing enhancer activity redundantly with other factors which are controlled by LIF (such as Esrrb)—in this case, its activatory role can only be appreciated in the absence of LIF; 4/ Nanog and LIF act in parallel to sustain H3K27me3 at differentiation genes such as Otx2. This latter role of Nanog is particularly important in the context of Nanog-mediated, LIF-independent self-renewal