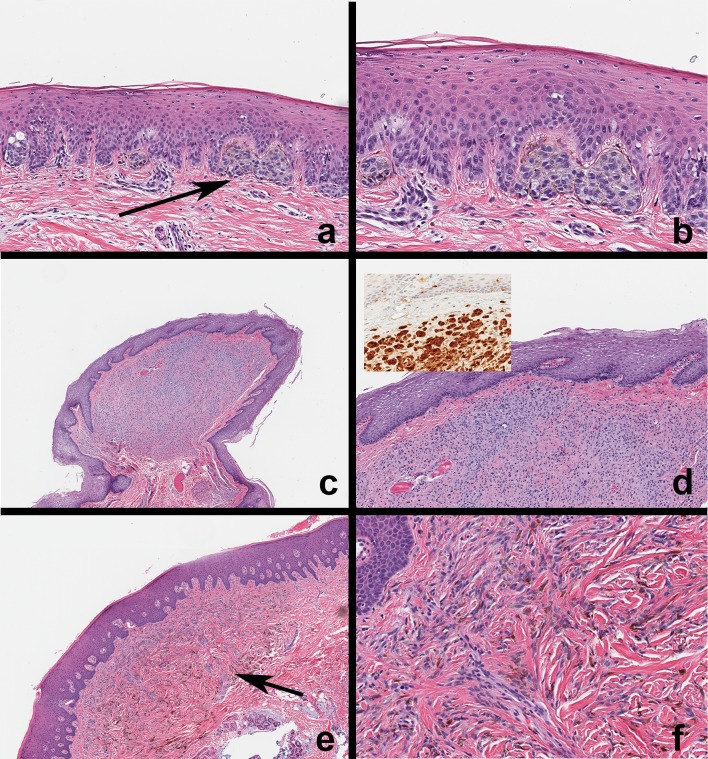
Fig. 4.
Microscopic features of oral mucosal nevi. a, b Compound nevus. Note nevocyte nests at the junction of the epithelium and lamina propria with intracytoplasmic melanin pigmentation. Nevocytes arranged in theques exhibit banal nuclear features. c, d Intramucosal nevus. This is a discrete nodule with no evidence of junctional nevocyte activity. Nevocytes exhibit maturation from the surface taking on a neurotized morphology deeper in the submucosa. Nevocytes exhibit S-100 expression (inset). e, f Common blue nevus. Nevocytes within the connective tissue (arrow); note the absence of junctional activity and theque formation. Nevus cells are spindle shaped, exhibit banal cytology, contain melanin pigment, and often arranged parallel to the surface epithelium; this distribution and the Tyndall effect corresponds to the blue-black appearance of these lesions