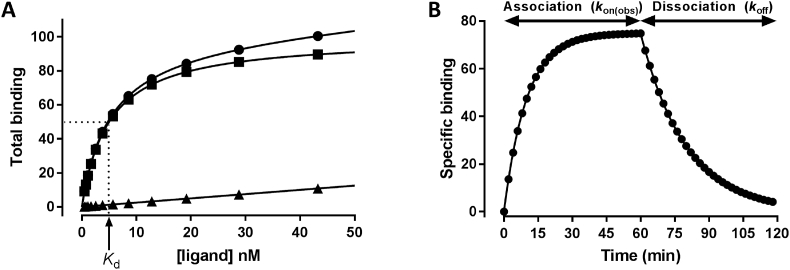
Fig. 1.
Simulated saturation and kinetic binding curves. Saturation and kinetic binding curves were simulated in GraphPad prism assuming R + L ⇋ RL using the one site: total and non-specific binding equation (A) or association then dissociation equation (B) for a ligand with a Kd of 5nM (A) or 50nM (B). For (A), the specific binding (squares) Bmax was set to 100 and Kd to 5 nM and the non-specific binding (triangles) set to a slope of 0.25. For (B) the kon was set to 1 × 106 M−1 min−1 and koff to 0.05 min−1, the concentration of ligand to 50 nM and the BMAX to 150, which results in a Kd of 50 nM. The association phase of the kinetic binding curve is termed kon(obs) and is defined as kon = (kon(obs)-koff)/[ligand].