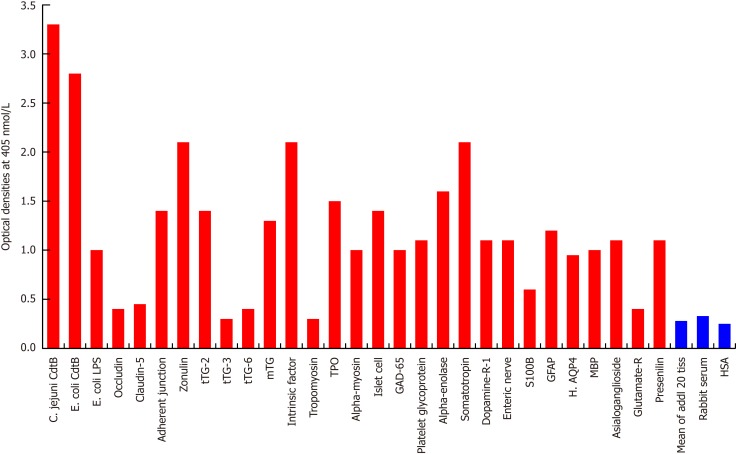
Figure 3.
Reaction of affinity-purified rabbit anti-Campylobacter jejuni cytolethal distending toxin with different tissue antigens. Compared to the reaction with Campylobacter jejuni (C. jejuni) cytolethal distending toxin (Cdt) as positive control and human serum albumin (HSA) or unimmunized rabbit serum as negative control, the reaction of this antibody with 20 tissue antigens is insignificant, with an additional 5 tissue antigens slightly higher than the mean of the 20 but still insignificant; with Escherichia coli (E. coli) lipopolysaccharide (LPS), α-myosin, claudin-5 and 8 different neuronal or associated antigens (enteric nerve, S100B, AQP4, myelin basic protein, asialoganglioside GM1, presenelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase-65) is low, with adherent junction, transglutaminase-2, microbial transglutaminase, thyroid peroxidase, islet cell, a-enolase, glial fibrillary acidic protein, dopamine-R1, and platelet glycoprotein is moderate, with somatotropin, intrinsic factor and zonulin is high, and with E. coli Cdt is very highly positive. The variation of quadruplicate ODs was less than 10% for all determinations. Comparison of the means of the antibody reactivity to various food antigens with the means of controls resulted in insignificant values (P > 0.05) for 25 different tissue antigens and highly significant P values (P < 0.00001) for the other antigens. E. coli: Escherichia coli; Cdt: Cytolethal distending toxin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; tTG: Transglutaminase; mTG: Microbial transglutaminase; DPPIV: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; TPO: Thyroid peroxidase; GAD-65: Glutamic acid decarboxylase-65; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; H. AQP4: Human aquaporin-4; MBP: Myelin basic protein; Glutamate-R: Glutamate receptor; HSA: Human serum albumin.