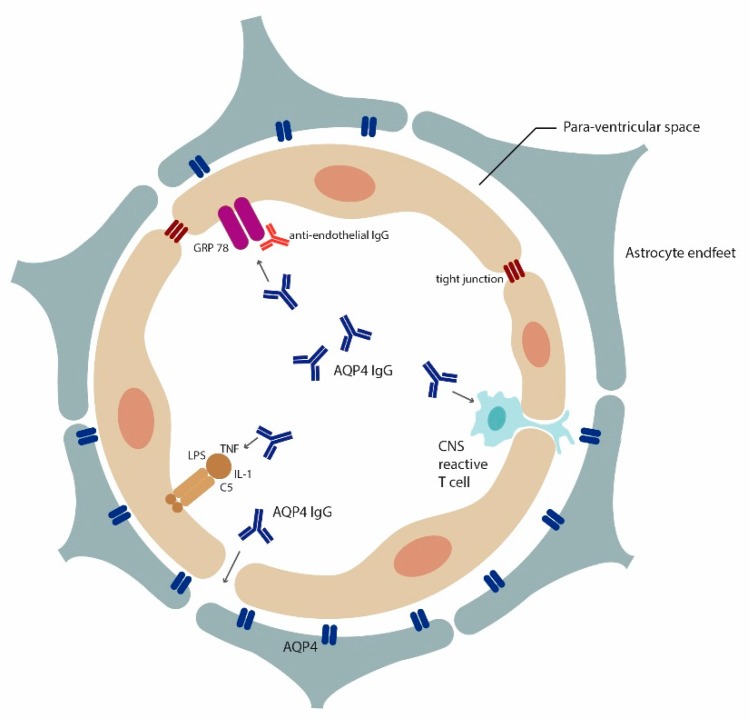
Figure 1.
Multiple mechanisms for AQP4-IgG access to the brain: Insights from rodent models. Cross section of a blood vessel demonstrating how AQP4-IgG can enter the brain according to findings from rodent models. BBB breach can occur through encephalitogenic CNS reactive T cells [59,60], inflammatory agents [67] (LPS, TNF alpha, IL-1) and antibodies that alter endothelial cells functional (e.g., anti-GRP78 antibodies [64]). Recently, it was postulated that high affinity AQP4-IgG could enter the brain through circumventricular organs and meningeal or even parenchymal blood vessels without prior BBB insult [65].