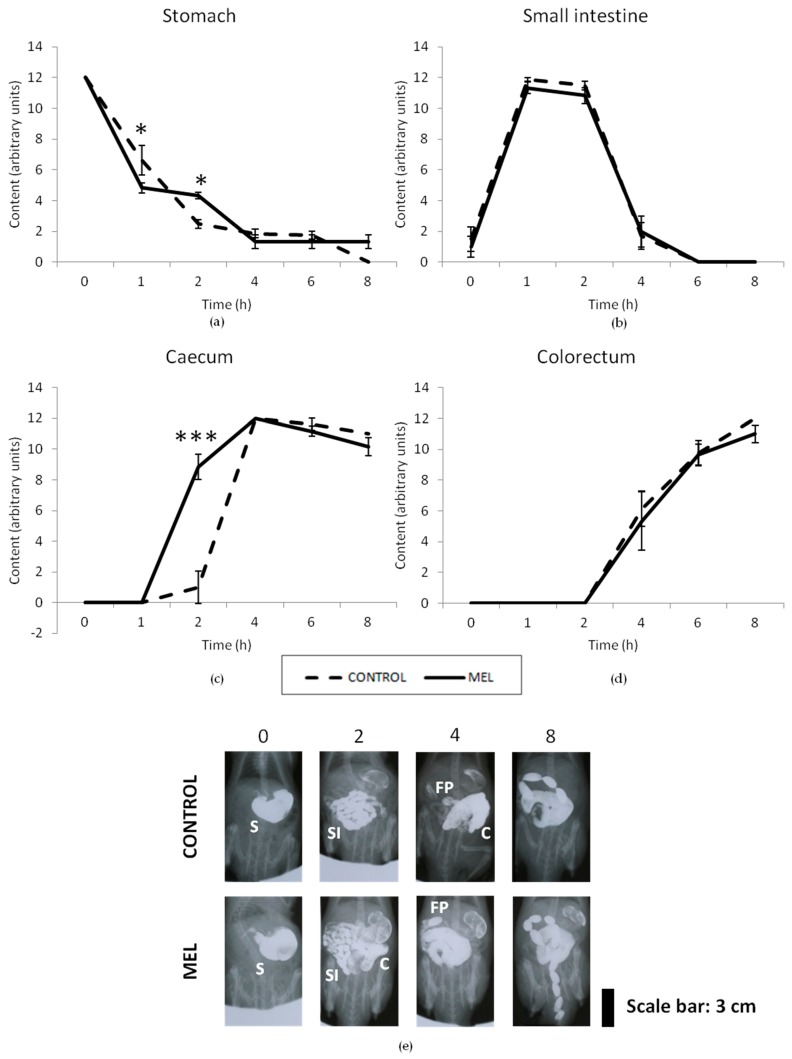
Figure 4.
Radiological analysis of gastrointestinal motor function in rats—a semiquantitative analysis. A dose of barium sulfate (3 mL, 2 g/mL) was intragastrically administered at time 0, and X-rays were taken immediately and 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h, after administration. Motility curves for the stomach (a), small intestine (b), caecum (c), and colorectum (d) were obtained from the control rats (n = 8) and rats treated with MEL (4 g/L) (n = 6). Data represent the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 (Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test). Representative X-rays (e) obtained from a control and a MEL-treated rat at 0, 2, 4, and 8 h, after administration of barium sulfate. S—stomach; SI—small intestine; C—caecum; FP—fecal pellets (within the colorectum).