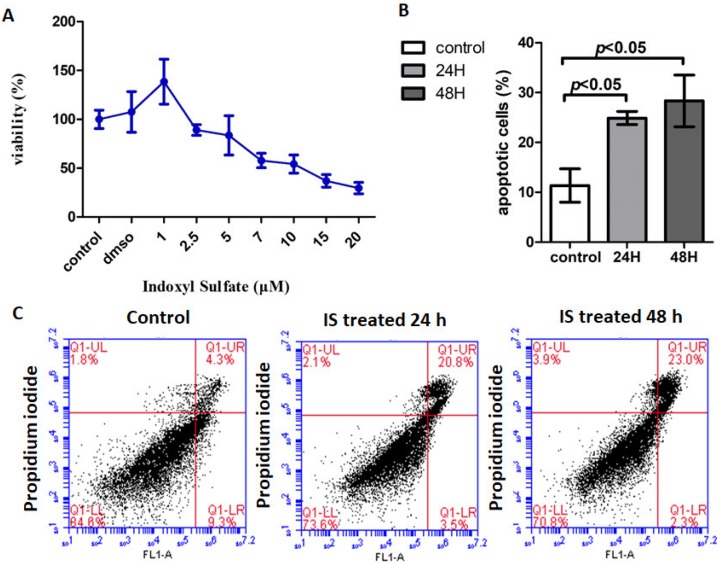
Figure 2.
The cellular toxicity of IS treated human astrocyte. (A) Effect of IS on cell viability of human astrocytes. Cell viability was assessed with WST-1 assay after 72 h of treatment with different concentrations of IS. The cell toxicity of IS was found to be dose dependent. Exposure to 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 15, and 20 μM IS decreased cell viability. The graph represents mean cell viability (%) ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. (B) IS induced human astrocyte apoptosis at 24 h and 48 h compared to control. (C) Human astrocytes were treated in either control or IS for 24 h and 48 h. The results were analyzed using a flow cytometer with fluorescein-isothiocyanate-conjugated Annexin V and propidium iodide stain. Increased apoptosis was noted in the astrocytes treated with IS for 24 h and 48 h.