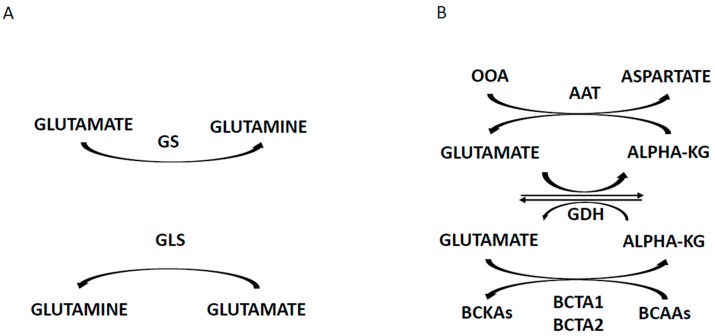
Figure 5.
Main steps of glutamine metabolism. (A) Glutamine enters the cells via the SCL1A5 transporter (not shown) and contributes directly to nucleotide synthesis (not shown) or is converted to glutamate by glutaminase (GLS); the opposite reaction, the conversion of glutamate to glutamine, is catalyzed by glutamine synthetase (GS). (B) Glutamate is converted to α-ketoglutarate (alpha-KG) by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) or by aminotransferases (AAT).