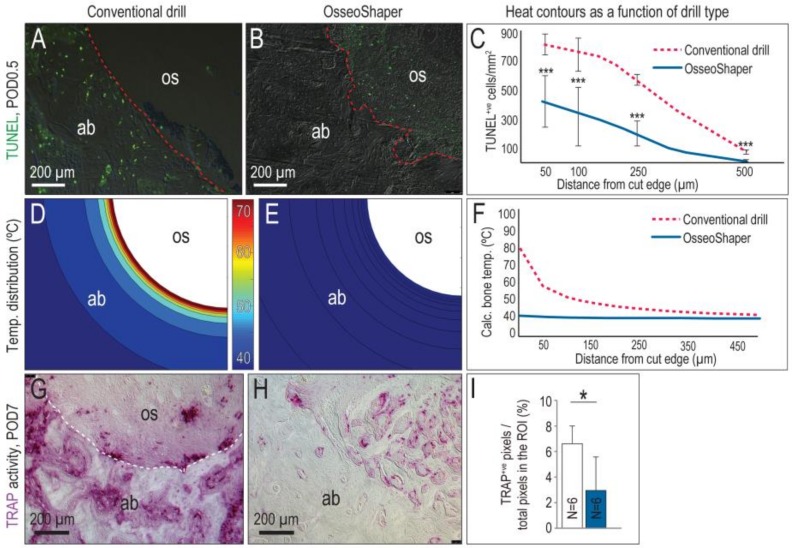
Figure 3.
The OsseoShaper generates less heat, which results in a smaller zone of cell death and less tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-mediated bone remodeling than conventional drills. (A) Representative tissue section from an osteotomy prepared using standard drills, where terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end labeling (TUNEL)+ve cells are apoptotic osteocytes. (B) Equivalent tissue section from an osteotomy prepared using the OsseoShaper, where the majority of apoptotic cells are detected in the osseous coagulum. (C) Distribution of TUNEL+ve cells as a function of distance from cut edge of osteotomy. Computational models were used to map the distribution of heat in bone as a function of distance from the cut edge, in osteotomies produced using (D) conventional drills and (E) using the OsseoShaper. (F) Calculated temperatures in bone, expressed as a function of radial distance from conventional drills (dotted red line) and from the OsseoShaper (blue line) (N = 6). (G) Representative transverse tissue section from an osteotomy produced with conventional drills, analyzed on for TRAP activity on post-osteotomy day 7 (POD7). (H) TRAP activity on a representative transverse tissue section from an OsseoShaper-produced osteotomy. (I) Quantification of TRAP+ve pixels/total pixels in the region of interest (ROI). A dotted line is used to indicate the cut edge of the osteotomy. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. Scale bars = 200 μm. Abbreviations: as indicated previously.