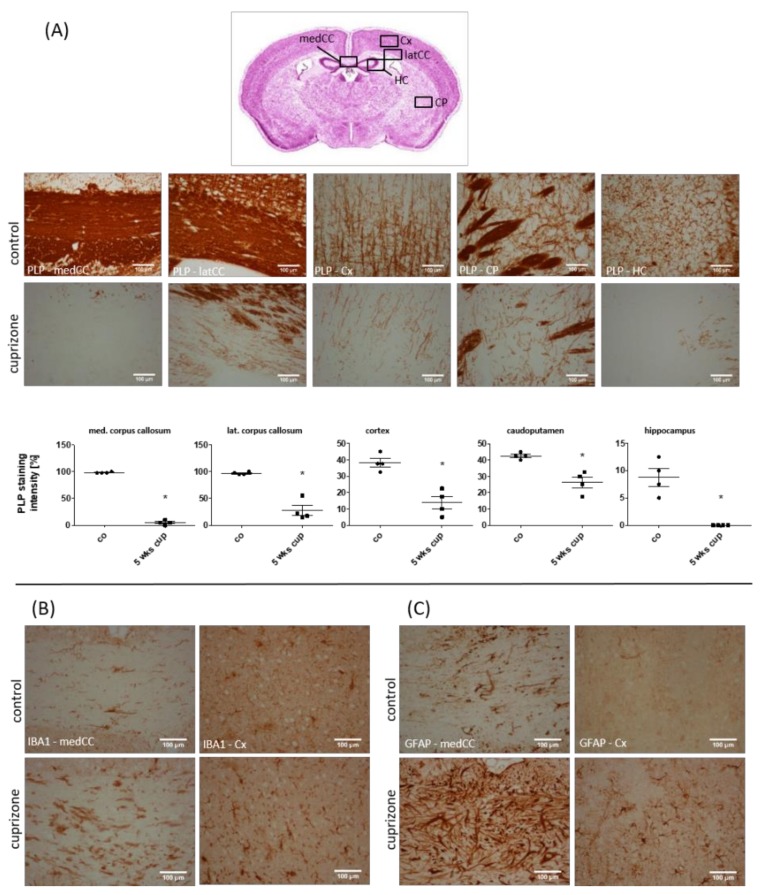
Figure 1.
Cuprizone-intoxication induces multifocal demyelination and reactive glia activation. (A) The myelination of different brain areas, determined by anti-PLP staining. The upper row shows representative pictures of the control (n = 4), and the lower row shows representative pictures of the cuprizone-intoxicated animals (5 weeks; n = 4). (B) Cuprizone-induced demyelination is paralleled by microglia activation (shown with IBA1 immunoreactivity; n = 4), and (C) astrocyte activation (shown with GFAP immunoreactivity; n = 4). medCC (medial part of the corpus callosum); latCC (lateral part of the corpus callosum); Cx (cortex); CP (caudoputamen); HC (hippocampus). Differences were determined using Mann–Whitney tests. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001.