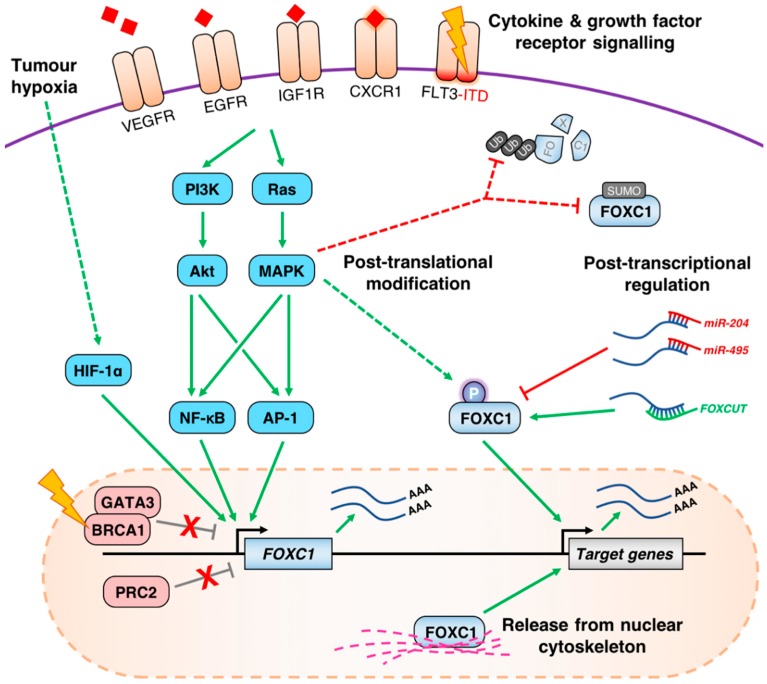
Figure 2.
A summary of known pre-/post-transcriptional and post-translational processes regulating FOXC1 in cancer. Across several malignancies, deregulation of diverse membrane-associated receptors by mutation and/or overexpression leads to hyperactivation of the MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways and frequent induction of FOXC1 transcription via downstream TFs including AP-1 and NF-κB. In hypoxic tumors, activation of HIF-1α may further stimulate FOXC1 expression. These processes may occur in parallel with loss of PRC2 or BRCA1/GATA3-mediated repression of FOXC1 through currently unclear mechanisms. FOXC1 mRNA may be further regulated through the action of ncRNAs including FOXCUT and miR-204/miR-495 which enhance or impede translation into FOXC1 protein, respectively. Finally, the transcriptional activity and stability of FOXC1 protein may be modulated by partitioning in the nuclear cytoskeleton, or by post-translational modifications including phosphorylation and SUMOylation, although the contribution made by these processes to cancer-specific functionality of FOXC1 remains unclear.