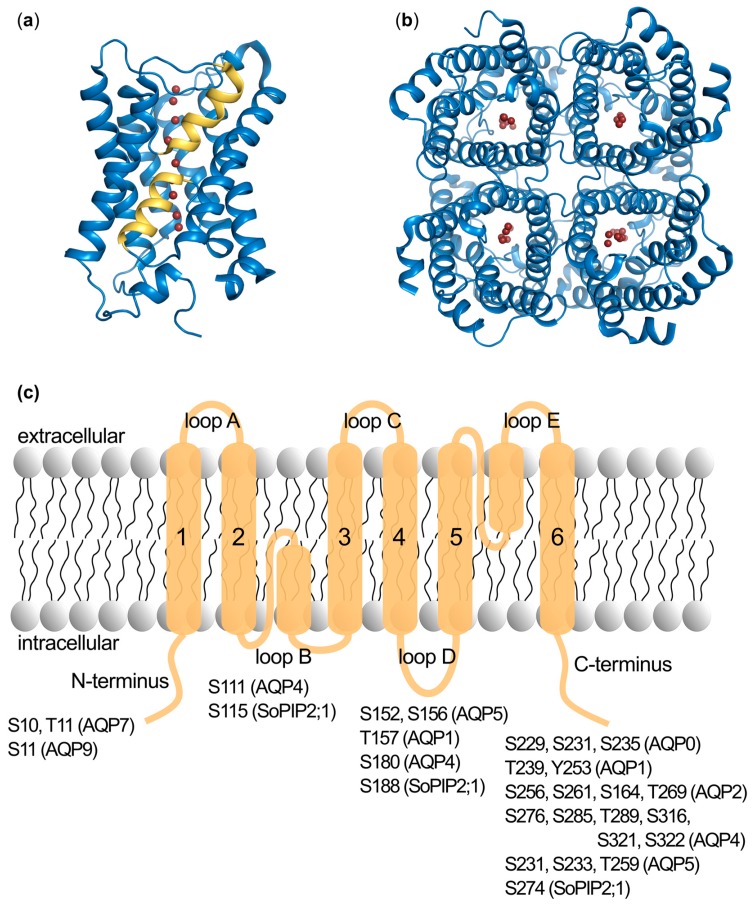
Figure 1.
The overall structure of aquaporins and the localization of individual phosphorylation sites. (a) Side view of the aquaporin monomer represented by the crystal structure of human AQP5 (PDB 3D9S). Water molecules in the water-conducting pore are marked as red spheres. The two half-helices formed by loops B and E are coloured yellow. (b) The tetrameric assembly from the cytoplasmic side. (c) A schematic representation of the aquaporin topology with all phosphorylation sites identified in mammalian aquaporins as well as the spinach aquaporin SoPIP2;1 marked.