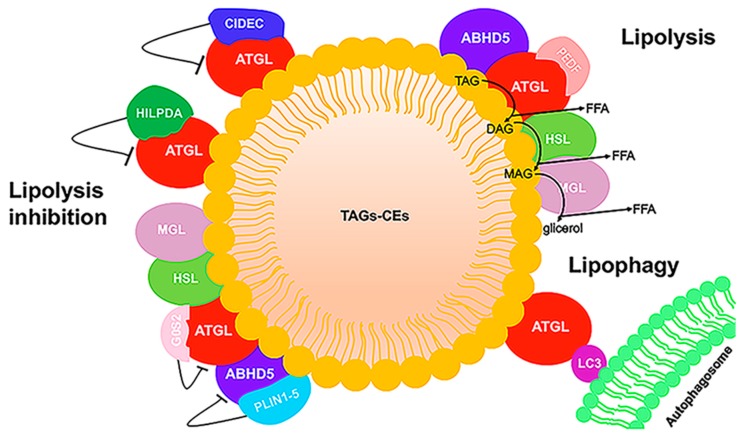
Figure 4.
LD schematic representation. LDs have a core composed of triacylglycerol (TAG) and cholesteryl ester (CE), surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer. Some proteins binding to the phospholipid monolayer are involved in neutral lipid metabolism. In the stimulated condition, ABHD5 binds to and activates ATGL, and TAG is hydrolyzed sequentially by ATGL, hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and monoacyl-glycerol lipase (MGL) to generate fatty acid (FA) and glycerol. In hepatic and muscle cells, pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) stimulates lipolysis by binding ATGL. In the unstimulated state, lipolysis is inhibited by the association of ATGL with G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2), hypoxia-inducible LD-associated protein (HILPDA), and cell death activator CIDE-3 (CIDEC) and by the interaction between ABHD5 and perilipin (PLIN) proteins. In addition, ATGL can interact with LC3, an autophagic protein. Direct ATGL–LC3 binding can facilitate correct ATGL localization on the LD surface.