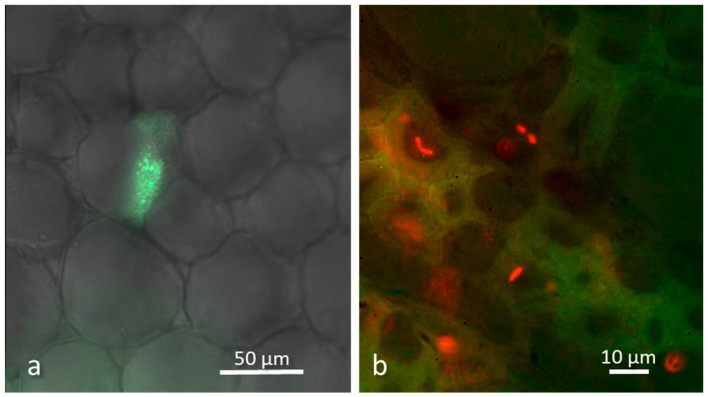
Figure 1.
Confocal microscopy images of experimentally inoculated plants showing the ability of endophytic bacteria to inhabit a new host (a) Burkholderia sp. isolated from grapevine leaf tissues [76] and transformed with green fluorescent protein is able to sustain bacterial cell division in periwinkle parenchyma stem cells. (b) Pantoea agglomerans isolated from orchids and transformed with red fluorescent protein [77] has been inoculated via root absorption in apple plantlets: bacterial cells are visible in the upper leaves after two weeks from inoculation, demonstrating the ability to stably colonize a different host.