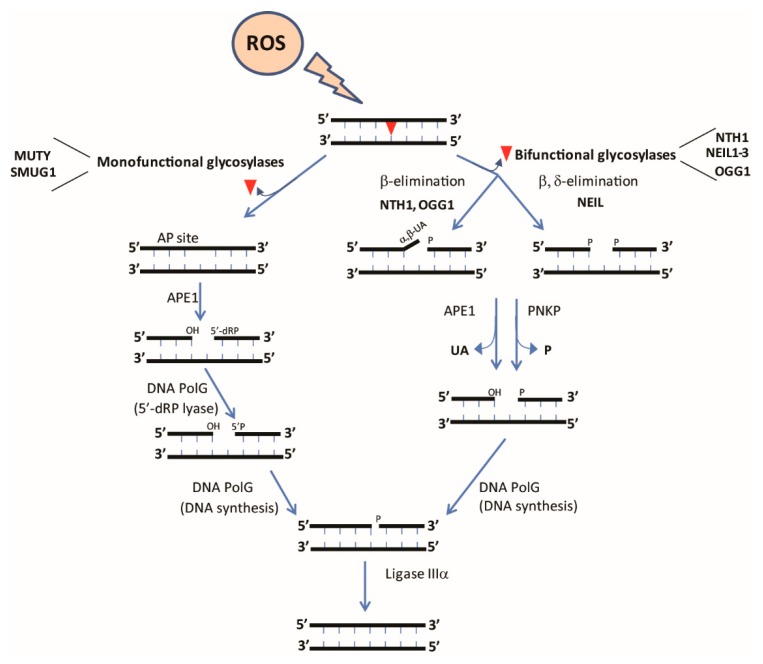
Figure 2.
Base Excision Repair (BER) in mitochondria. Generation of free radicals induces DNA lesions in the form of oxidized bases, affecting base-pairing properties. Oxidative lesions are repaired via the BER pathway. BER is initiated by the activity of DNA glycosylases such as monofunctional glycosylases which recognize and cleave the N-glycosidic bond between the modified base and sugar, creating an abasic site and bifunctional glycosylases which have an additional intrinsic Apurinic/Apyrimidinic (AP)lyase activity. The incision of the AP site occurs via β elimination or β-δ elimination which is further processed by APE1 or PNKP, followed by gap-filling by DNA pol gamma (PolG). Once the AP site has been processed and the correct nucleotide recruited by PolG, the free DNA ends are ligated by DNA ligase III (LIG3).