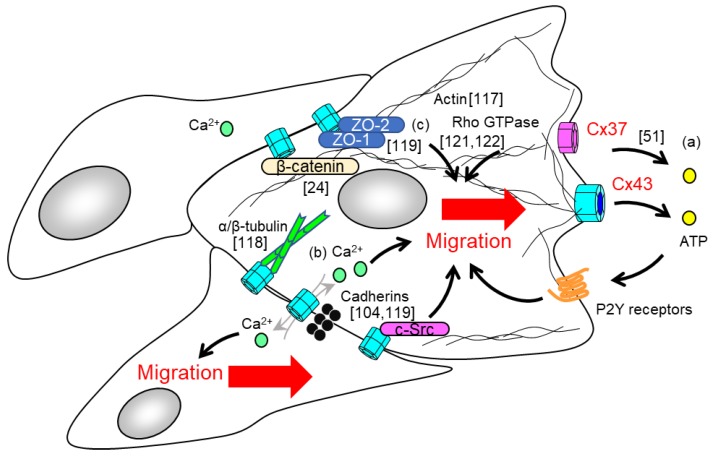
Figure 2.
Endothelial Cx-dependent regulation of cell migration in angiogenesis. Gap junctions and Cxs regulate cell migration via channel function dependent and independent pathways. (a) Extracellular ATP released by Cx-hemichannels activates P2Y receptors, which trigger cell migration [48]. (b) Gap junction-mediated propagation of calcium waves is required for collective cell migration. (c) The interaction of Cx and gap junction with cytoskeletal proteins or intracellular proteins orchestrates cytoskeletal rearrangement and cell migration [24,116].