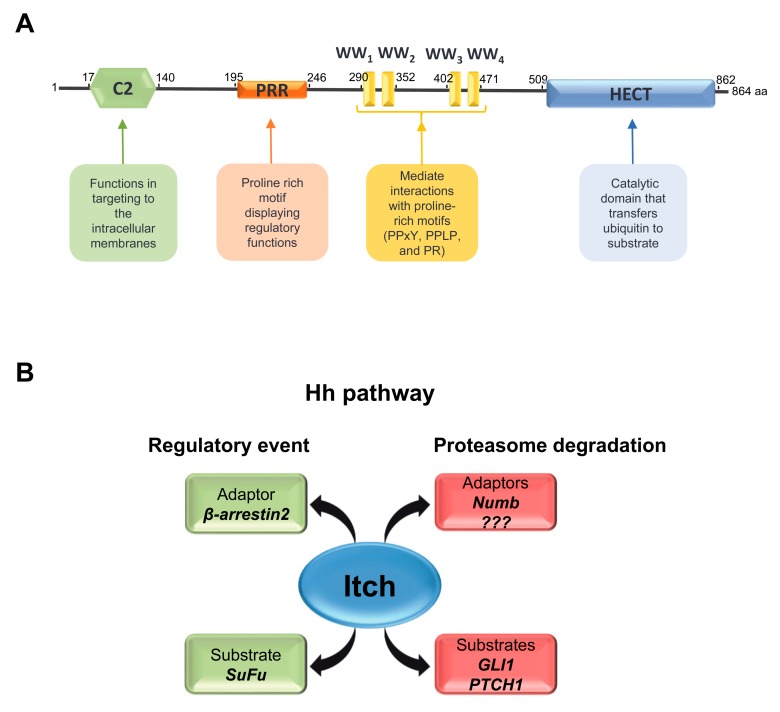
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the modular structure of Itch and its involvement in Hh pathway regulation. (A) Itch protein consists of an N-terminal Ca2+/lipid-binding (C2) domain (green hexagon), a proline rich motif (orange rectangle) displaying regulatory functions, a central region containing four WW domains (yellow bars) involved in protein-protein interaction and a catalytic HECT domain (blue rectangle). (B) The scheme shows the substrates of Itch involved in the regulation of Hh pathway (SuFu, GLI1 and PTCH1). Itch mediates regulatory events on SuFu and proteasome degradation on GLI1 and PTCH1 by the interaction with the adaptor proteins β-arrestin2 and Numb, respectively.