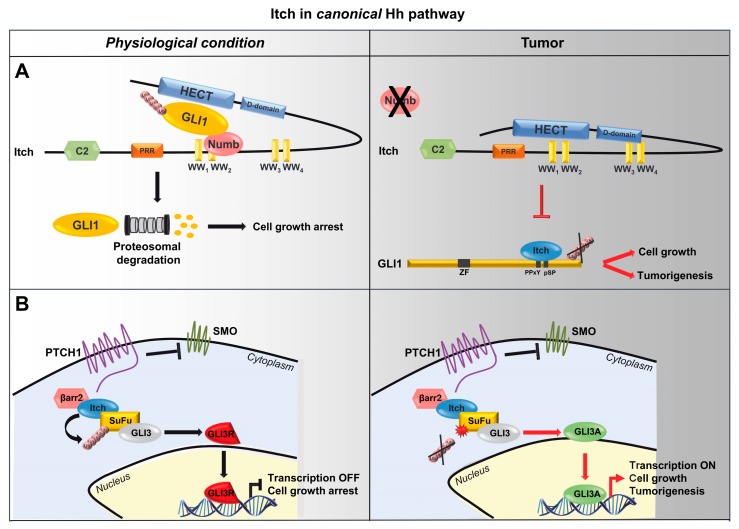
Figure 3.
Role of Itch in canonical Hh pathway. (A) Model of the Numb/Itch-dependent regulation of GLI1 activity. Numb binds WW2 domain of Itch, releases Itch from its close-inactive conformation, thus allowing the recruitment of GLI1 and its degradation. In cancer, loss of Numb impairs this process enhancing GLI1 activity and promoting cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. (B) Model of the β-arrestin2/Itch-dependent regulation of the SuFu function. Itch, in complex with β-arrestin2, binds and ubiquitylates SuFu. This event does not lead to SuFu degradation but increases the association between SuFu and GLI3 promoting the generation of GLI3 repressor form (GLI3R) and inhibiting Hh signalling. Alterations in this mechanism, caused by SuFu mutations that make it insensitive to Itch-dependent ubiquitylation, are responsible for MB development.