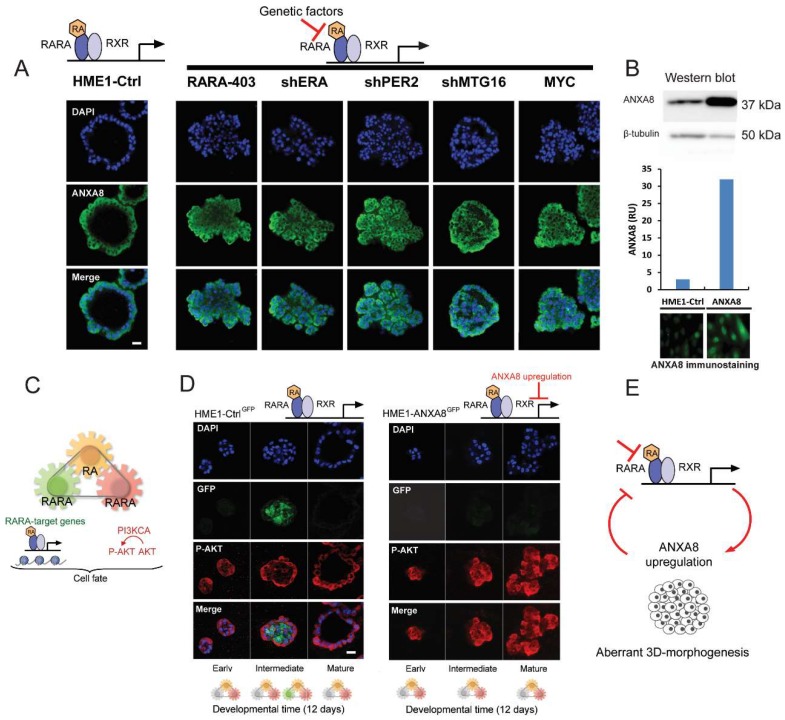
Figure 9.
HME1-Ctrl cells with a normal RA-RARA signaling grown in reconstituted basement membrane (Matrigel) culture develop 3D ductal acinar structures with a lumen lined by ANXA8 expressing cells within 12 days (A, left). HME1 cells with genetic mutations that hinder RA-RARA signaling form ductal acinar structures with a lumen filled with ANXA8 expressing cells (A, right);scale bar: 10µm. Western blot and immunostaining show higher expression in HME1-ANXA8 cells stably expressing ectopic ANXA8 relative to HME1-Ctrl cells (B). Scheme of the three module mechanism whereby physiological RA (yellow) coordinates via distinct RARA functions the spatiotemporal regulation of RARA transcription (green) and PI3KCA regulation of P-AKT signaling pathway (red) (C), HME1-CtrlGFP cells with normal RA-RARA signaling- stably expressing a RARE-GFP construct- show P-AKT (red) positive cells at all stages of 3D acinar morphogenesis, but express only GFP (green) in luminal cells at intermediate stage (D, left). HME1-ANXA8GFP cells show that ectopic ANXA8 expression affect the RA-regulation of RARA transcriptional function, but not the PI3K-AKT function regulated by RA, since cells are marked only by P-AKT at all stages of 3D morphogenesis (D, right); scale bar: 10 µm. Factors that hinder the physiological RA-RARA transcriptional mechanism by inducing ANXA8 expression reinforce a vicious circle of aberrant 3D morphogenesis (E).