Figure 1.
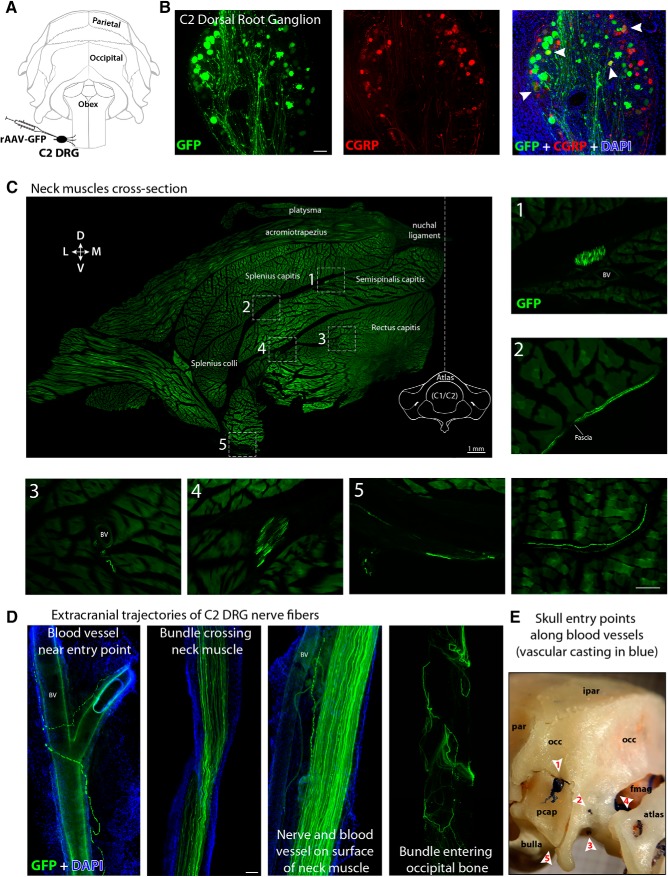
Anterograde tracing of C2 DRG peripheral axons to the posterior dura (extracranial component). A, Illustration of the rat's skull view from behind showing intra-ganglionar injection of rAAV-GFP viral vector into C2 DRG. B, Transversal view of a C2 DRG section showing GFP expression in successfully transduced cells (green, left), some of which were also immunoreactive to CGRP (red, middle). Superimposition of these images and DAPI (blue) is displayed at the right with white arrowheads indicating double-labeled cells (yellow). C, Cross-section of the whole neck at the level of C1 vertebra showing the distribution and trajectories of GFP-labeled nerves and fibers traveling along blood vessels (BV), fascia, and muscle from C2 DRG to the cranium. The image shows the left dorsolateral quadrant of the neck and was created by stitching 268 high-resolution images into a single composite. Numbers and frames indicate the areas where the images displayed at the right and bottom were taken. The only not-numbered image was taken from another cross-section of the neck in the same animal. D, Cervical nerves and bundles of fibers expressing GFP were observed crossing neck muscles, traveling along blood vessels and fascia before entering the cranium in the occipital region through (E) a canal between the occipital bone (occ) and the periotic capsule (pcap) (1), emissary canals near the occipital condyle (2), the hypoglossal canal (3), foramen magnum (fmag) (4), and jugular foramen (5). Interparietal bone (ipar), parietal bone (par). Scale bars, 100 μm.