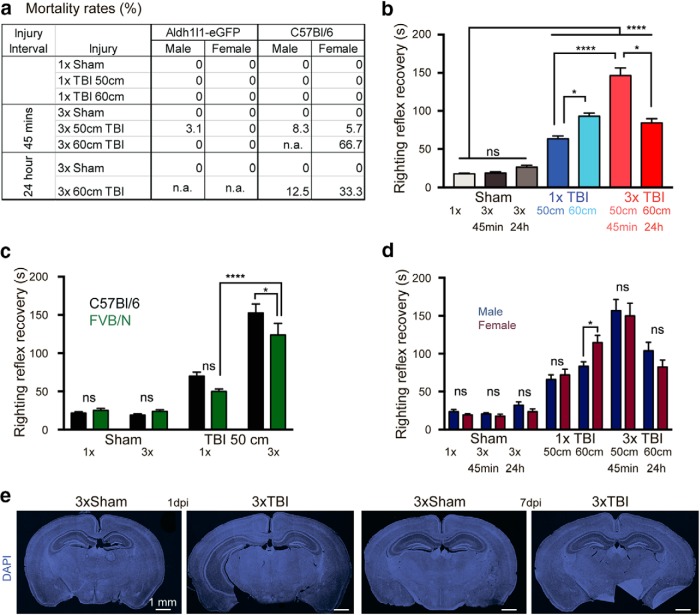
Figure 1.
Mild/concussive TBI induced LOC but presented without obvious tissue damage in C57BL/6 and FVB/N mice. a, Males and females displayed similar mortality rates when the 3× 50 cm 45 min TBI paradigm was used. Mortality rates for 3× 60 cm injuries were high. b, Increased injury severity and frequency as well as decreased interinjury intervals increased the length of the righting reflex recovery time as an indicator of LOC in C57BL/6 mice. c, C57BL/6 and FVB/N mice displayed comparable righting reflex recovery times after single TBI, but LOC was shorter in FVB/N mice after rdTBI was induced. d, Sex did not affect the righting reflex recovery time after single or repetitive mild/concussive TBI (50 cm, 45 min interinjury interval) (rdTBI) in C57BL/6 mice. e, Histology of the tissue using DAPI staining showed that rdTBI did not cause obvious tissue damage or loss. See Figure 1-1 for breakdown of sample sizes dependent on sex for representative images and detailed numerical data for all statistical group comparisons. *p ≤ 0.05, ****p ≤ 0.0001.