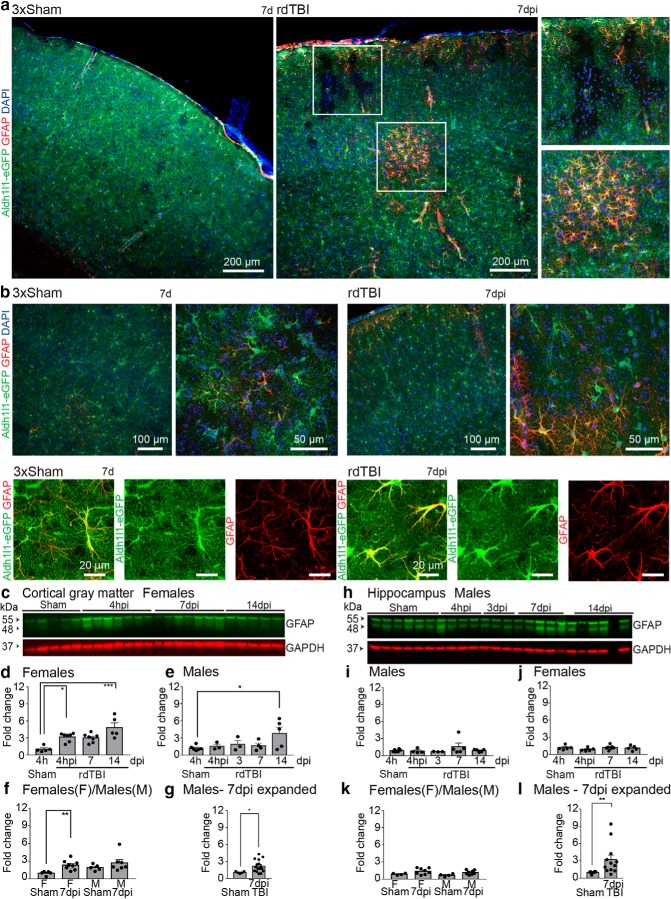
Figure 2.
rdTBI caused mild upregulation of GFAP and hypertrophy in a subset of astrocytes. a, rdTBI resulted in small groups of astrocytes scattered across the cortical gray matter that expressed GFAP at 7 dpi. Gray matter astrocytes in the forebrains of uninjured adult mice tile, resulting in an even distribution of Aldh1l1-eGFP reporter-positive astrocytes (3xSham, 7 d). After rdTBI, astrocytes disappeared or downregulated expression of the Aldh1l1-eGFP reporter (see also Fig. 4) indicated by areas with reduced levels of Aldh1l1-eGFP 7 dpi (rdTBI, and upper inset). b, Astrocytes with upregulated GFAP showed swelling of processes compared with GFAP positive astrocyte in 3xSham at 7 dpi. c–l, GFAP levels were mildly increased after rdTBI. Western blot for GFAP in cortical gray matter of female mice at different time points after rdTBI (c; quantified in d for females and in e for males) compared male (f) and female (g) mice and increased male sample number. Western blot for GFAP in hippocampus ofmale mice at different time points after rdTBI (h; quantified in i for males and in j for females) compared male (k) and female (l) mice with increased male sample number. See Figure 2-1 for breakdown of sample sizes dependent on sex for representative images and detailed numerical data for all statistical group comparisons. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001.