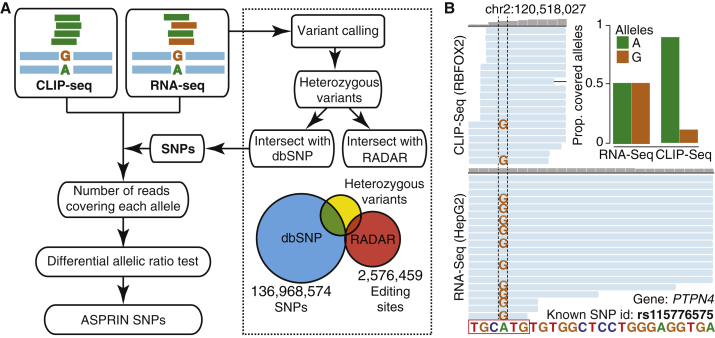
Figure 1.
The ASPRIN Pipeline for Identifying Allele-Specific Protein-RNA Interactions from CLIP-Seq and RNA-Seq Data
(A) Flowchart of the ASPRIN pipeline: variants are called from RNA-seq data, and heterozygous variants are intersected with dbSNP to obtain a list of high-confidence SNPs and intersected with RADAR to filter out potential A-to-I RNA editing events. For each SNP, ASPRIN counts the number of reads in the CLIP-seq and RNA-seq data that support each allele. An allelic ratio test then assesses whether one allele is significantly more preferred for RBP binding.
(B) An A-to-G SNP (rs115776575) disrupts a consensus RBFOX2 binding site in PTPN4. This disruption of binding is illustrated in the difference in the numbers of reads containing each allele in CLIP-seq reads, while equal numbers of reads contain each allele in the RNA-seq data.