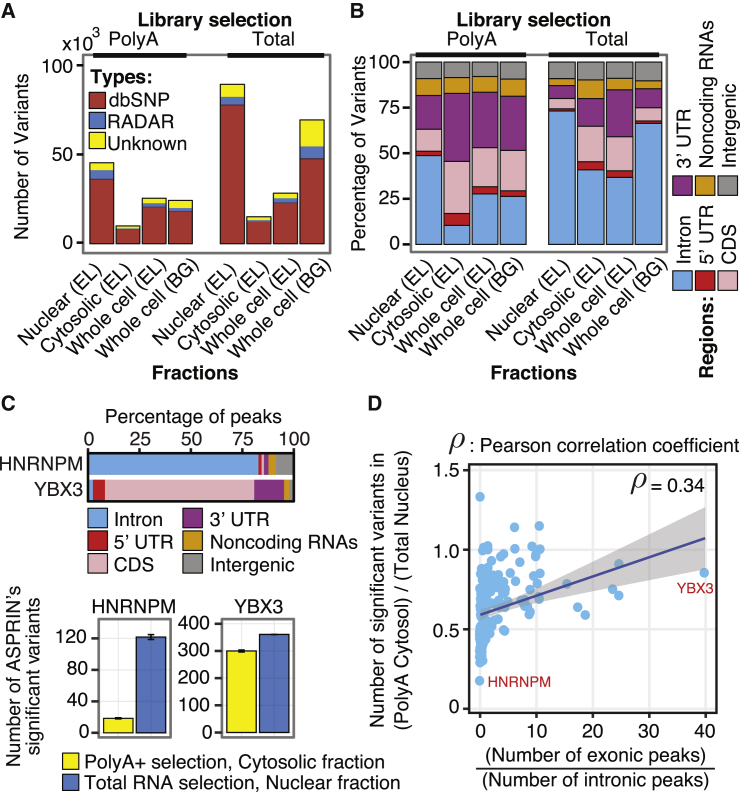
Figure 3.
RNA-Seq Variants Called from Different RNA-Seq Libraries of the HepG2 Cell Line
Two methods of library selection (polyA+ and total RNA) in different subcellular fractions (nucleus, cytosol, and whole-cell fractions from two different labs: EL = Eric Lecuyer’s lab at Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal, and BG = Brenton Graveley’s lab at University of Connecticut).
(A) Numbers of variants called from different RNA-seq libraries and their intersections with dbSNP and RADAR.
(B) Distribution of called variants in different genomic regions.
(C) Numbers of significant ASPRIN variants from polyA+ cytosolic or total RNA nuclear RNA-seq libraries for an RBP that binds predominantly to intronic regions (HNRNPM) and an RBP that binds predominantly to exonic regions (YBX3). Standard error of the mean is indicated as the error bar for each library selection method and subcellular fraction.
(D) The ratio of ASPRIN SNPs found using polyA+ cytosolic RNA-seq libraries to ASPRIN SNPs found using total RNA nuclear RNA-seq libraries increases as the ratio of exonic to intronic peaks increases.