Figure 2.
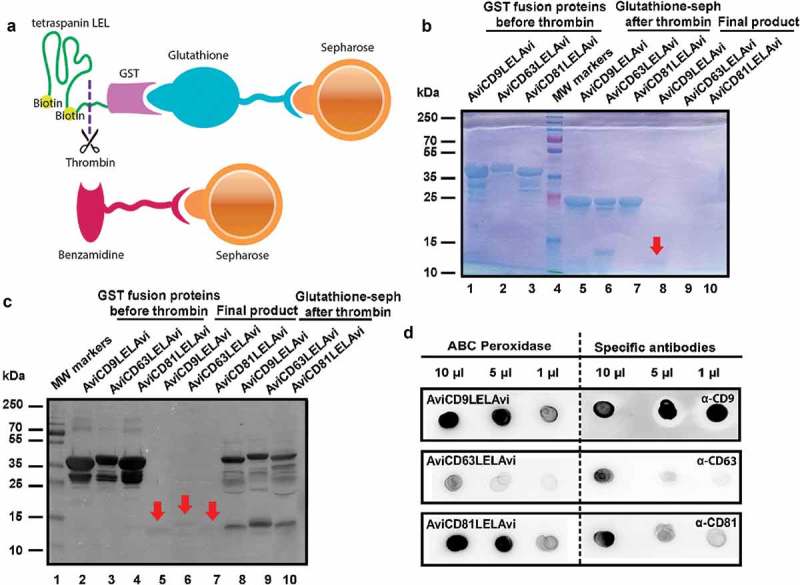
Production of recombinant tetraspanin-LELs. (a) Schematic illustration of the affinity chromatography method used for recombinant tetraspanin LELs purification using glutathione-sepharose beads, thrombin and benzamidine-sepharose beads. (b) Follow up of recombinant tetraspanin LELs production. The purification process was followed by Coomassie Blue staining after SDS-PAGE separation. Lanes 1–3: Samples of 10 µL Glutathione-sepharose beads before Thrombin treatment. Lanes 5–7: 10 µL of Glutathione-sepharose beads after treatment with Thrombin. Lanes 8–10: 20 µL of each supernatant after benzamidine-sepharose removal of Thrombin. Red arrows indicate the final LEL biotinylated product. (c) Western blot analysis of recombinant tetraspanin LELs. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and detected by chemiluminiscence using Avidin-Biotin-HRP Complexes. Lanes 2–4: Samples of 10 µL of AviLELAvi-GST of CD9, CD63 and CD81 coupled to Glutathione-sepharose. Lanes 5–7: Samples of 20 µL of AviCD9LELAvi, AviCD63LELAvi and AviCD81LELAvi. Lanes 8–10 Samples of 10 µL of Glutathione-sepharose beads after Thrombin treatment. Red arrows indicate the final LEL biotinylated product. (d) Dot blot immunodetection of recombinant tetraspanin LELs. The final products, biotinylated CD9, CD63 and CD81 LELs, were detected by Dot-blot using ABC Peroxidase Standard Staining Kit and monoclonal antibodies directed against CD9 (clone VJ 1/20), CD63 (TEA 3/10) and CD81 (5A6).
