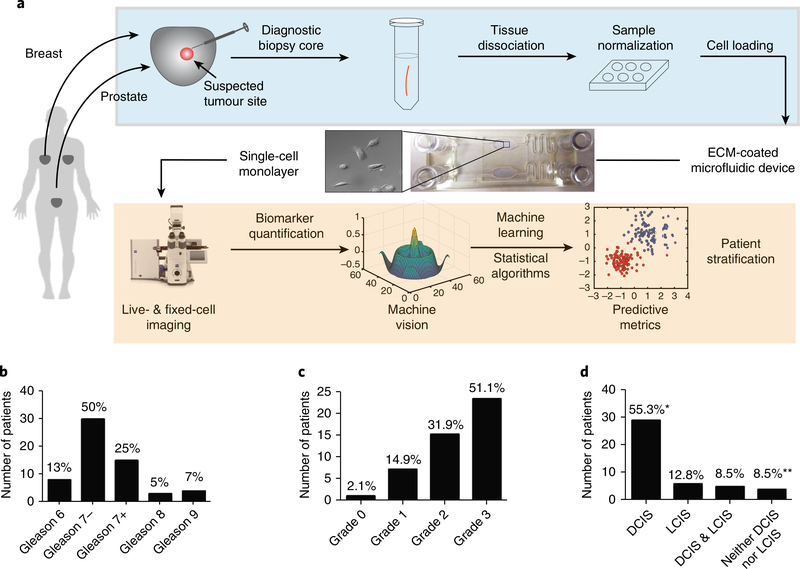
Fig. 1 |. Workflow for the risk stratification of patients via surgical adverse-pathology features using the live-primary-cell phenotypic-biomarker assay (STRAT-AP) and patient-sample characteristics of the clinical study.
a, Post-radical prostatectomy or mastectomy or lumpectomy biopsy cores were taken from tumour lesions at clinical collaborator sites. Cores were shipped overnight on cold packs to the central processing laboratory, and enzymatically dissociated. Cells were then cultured to normalize to in vitro conditions. Cells were imaged for a suite of phenotypic biomarkers via automated live-cell and fixed-cell microscopy on a microfluidic device. Images were analysed by machine-vision algorithms (processes in the orange shaded box are automated). The resulting data were objectively analysed by machine-learning statistical algorithms. b, Distribution of samples on the basis of Gleason score: 7−(Gleason 3+ 4) and 7+ (Gleason 4+ 3) samples (percentages of each Gleason score in the sample population are noted). The prostate sample set used in this study is representative of the naturally occurring distribution of Gleason scores found in the US population, according to initial biopsy reports. c, Grade distribution for the breast sample set. d, DCIS and LCIS distribution of the breast sample set. *Four samples were positive for DCIS yet did not have LCIS data reported. **Three samples were negative for DCIS yet did not have LCIS data reported. Image of microscope reproduced with permission from ZEISS Microscopy.