Figure 1.
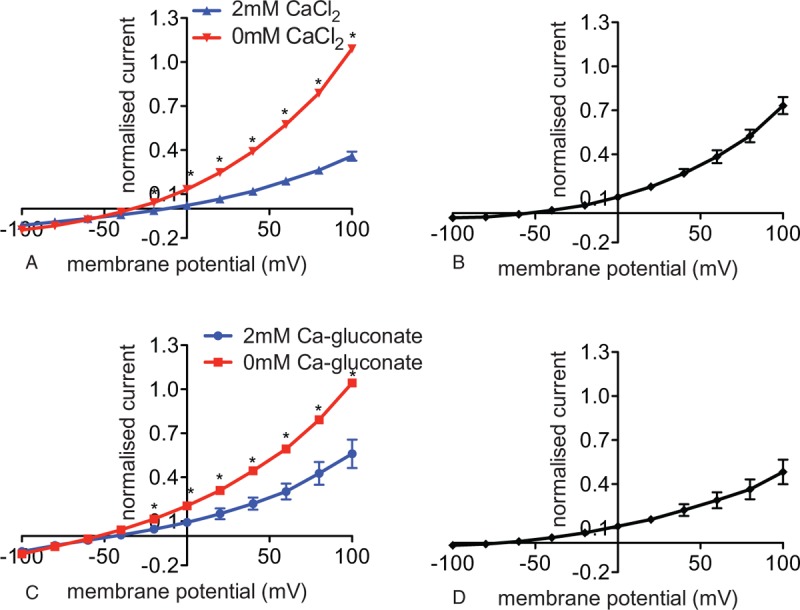
Detection and characterization of a CBC in red blood cells of healthy adults. Whole cell patch clamp recordings in a Cs+-based internal and a tetraethylammonium chloride-based external solutions. (A) I/V curves with 2 mM CaCl2 (blue) and 0 mM CaCl2 (red) in the external solution (n = 5 (3) with n being the number of cells and in brackets the number of donors). Reversal potential for the I/V curve recorded in 2 mM CaCl2 external solution (blue) is −13 mV and in 0 mM CaCl2 in the external solution (red) −33 mV. (B) I/V curve of the CBC—the current recorded in 2 mM CaCl2-external solution was subtracted from the current recorded in 0 mM CaCl2-external solution. Whole cell patch clamp recordings in a Cs+-based internal and a TEANO3-based external solution devoid of Cl−. (C) I/V curves with 2 mM Ca gluconate (blue) and 0 mM Ca gluconate (red) in the external solution (n = 4 (1) with n being the number of cells and in brackets the number of donors). Reversal potential for the I/V curve recorded in 2 mM Ca gluconate in the external solution (blue) is −44 mV and in 0 mM CaCl2 in the external solution (red) is −54 mV. (D) I/V curve of the CBC—the current recorded in 2 mM Ca gluconate-external solution was subtracted from the current recorded in 0 mM Ca gluconate-external solution. Currents were elicited by voltage steps from −100 to 100 mV for 500 milliseconds in 20 mV increments at Vh = −30 mV. Measurements were performed at room temperature. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean and as normalized currents (Supplemental Fig. 2, Supplemental Digital Content, gives currents in absolute values, in pAs). Significance is assessed with a paired Student t test and set at P < 0.05. For better visualization, a significance anywhere below P < 0.05 is denoted with 1 star. CBC = Ca2+-blocked current.
