Figure 1.
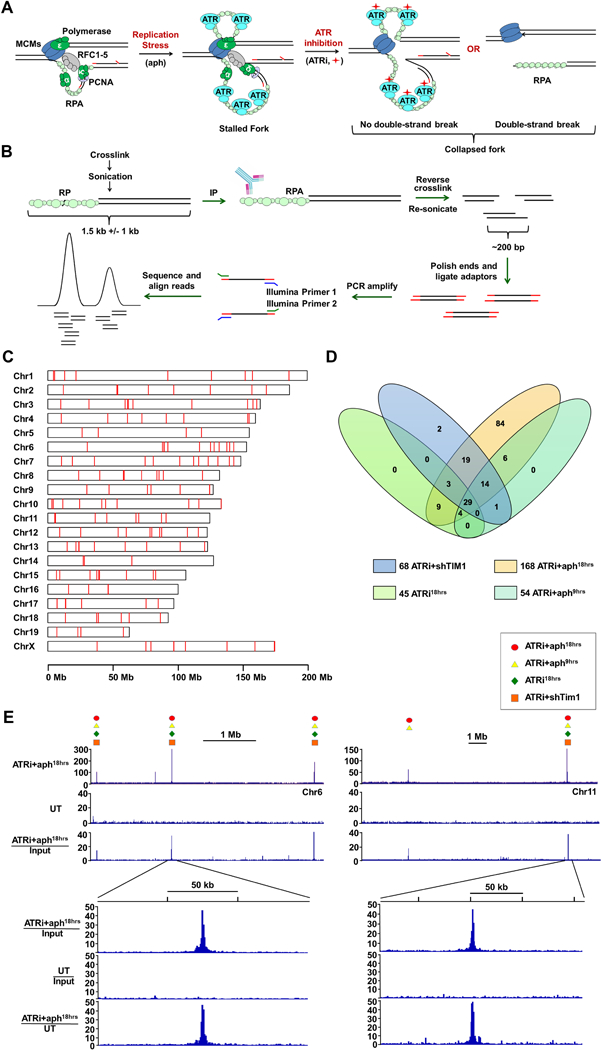
Genome-wide Identification of Fork Collapse Sites by RPA-ChIP Seq (A) RPA-ChIP Seq detection of replication fork collapse from ATR inhibition (ATRi, red diamond). (B) Schematic of RPA-ChIP Seq experimental approach. Cross-linked chromatin was sonicated into large fragments (1.5 kb average) prior to immunoprecipitation with RPA2 antibody. Retrieved DNA was sonicated into smaller fragments (200–300 bp) for NGS. (C) RPLs identified in the mouse genome (red marks). (D) Venn diagram depicting overlap of peaks identified from different conditions. (E) Representative peaks in RPA-ChIP Seq coverage and ratio tracks (ATRi+aph18hrs and DMSO-treated control, UT). Symbols above select peaks indicate identification under additional experimental conditions. See also Supplemental Table S1 and S2.
