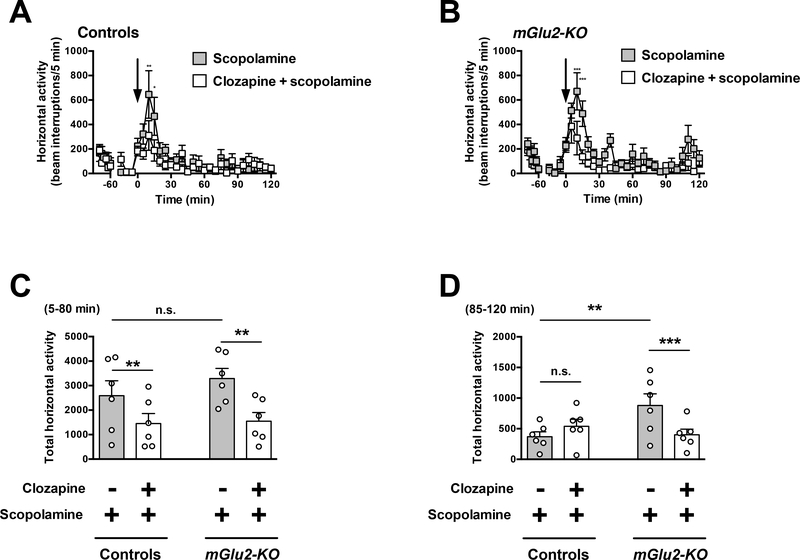
Fig. 7.
Effect of clozapine on scopolamine-induced locomotion. (A-D) Wild-type and mGlu2-KO mice were placed in the locomotor chamber and allowed to habituate for 90 min. After habituation, mice were injected with clozapine (1.5 mg/kg) or vehicle followed by scopolamine (2.0 mg/kg), and locomotor activity was measured for another 120 min (n = 6). (A,B) The panel depicts the time course of scopolamine-induced locomotion in 5 min blocks. Time of injection is indicated by arrow. (C,D) Data summary of the total scopolamine-induced locomotion as a summation of horizontal activity from t = 5 to t = 80 min (C) and from t = 85 to t = 120 min (D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Bonferroni’s post hoc test of two-way ANOVA. Data are means ± SEM, n.s., not significant.