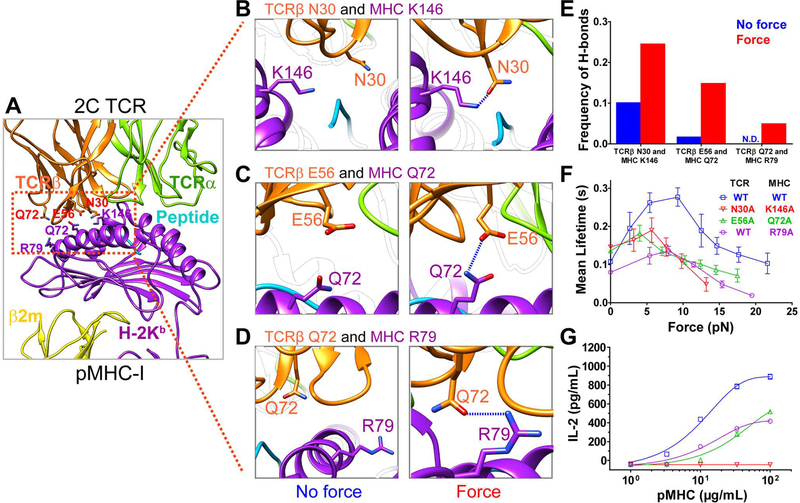
Figure 3. Force-strengthened H-bonds between MHC and TCR contribute to TCR-pMHC catch bonds and T cell responses.
(A-D) The location of residues involved in force-strengthtened H-bonds in SMD simulations (A). Representative snapshots of H-bond formations between TCRβ N30 and MHC K146 (B), between TCRβ E56 and MHC Q72 (C), and between TCRβ Q72 and MHC R79 (D) under force or no force. H-bonds are indicated as dashed blue lines. (E) The frequencies of forming H-bonds for above paired residues under force or no force. N.D., not detected. (F) Force-dependent bond lifetimes of WT or mutated 2C TCRs binding with WT or mutated R4-MHCs measured by the BFP. (G) IL-2 production from WT or mutated 2C hybridomas that were stimulated with WT or mutated R4-MHCs. Error bars in (F and G) represent SEM. See also Figure S3.