Figure 1.
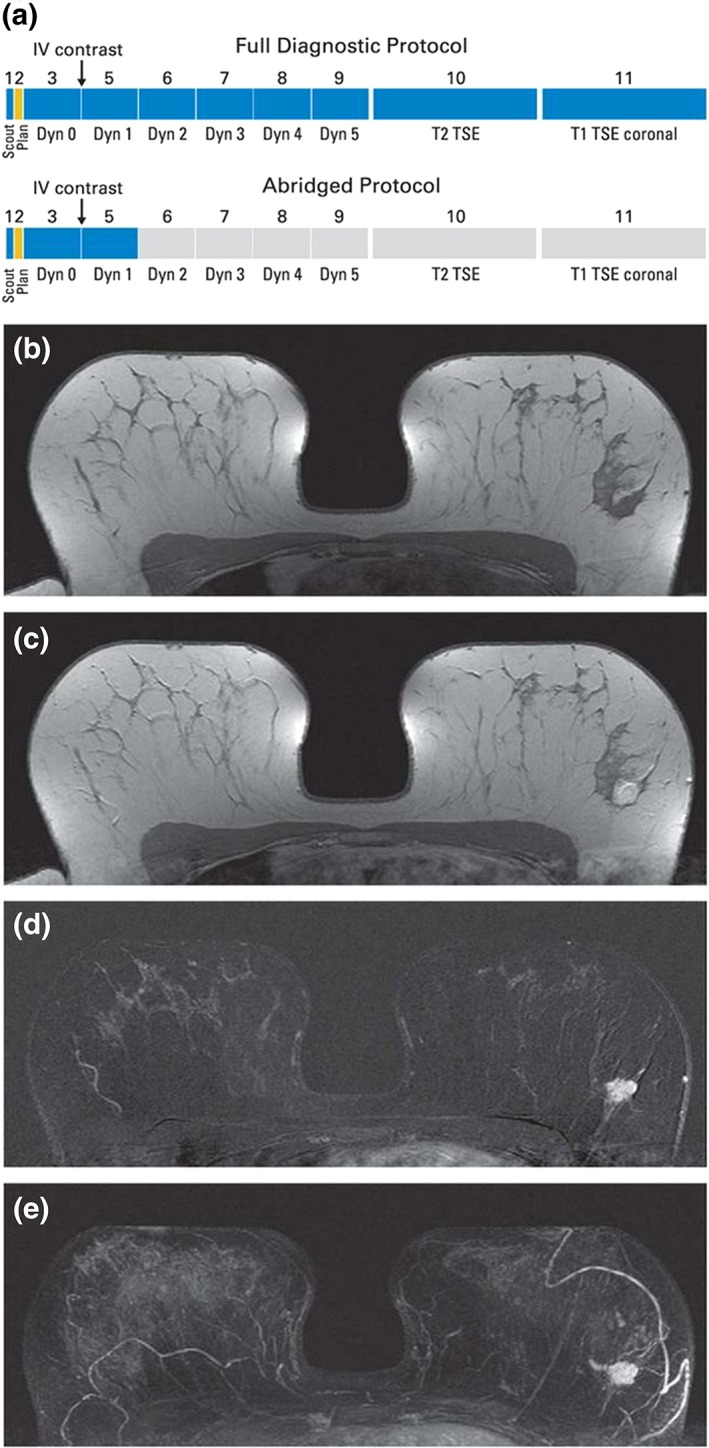
(A) Schematic presentation of full diagnostic and abbreviated protocols and (B–E) clinical example of calculation of first postcontrast subtracted (FAST) and maximum intensity projection (MIP) images in patient with left‐sided breast cancer. (B) Midbreast section of baseline (precontrast) dynamic acquisition (A; Dyn 0); (C) corresponding section of first postcontrast dynamic acquisition (A; Dyn 1); (D) corresponding FAST image, generated by subtracting image (B) from image (C); and (E) MIP image, generated by fusing all FAST sections into single 3D‐like projection image. Scout is automatic survey. Dyn refers to single dynamic acquisition consisting of image stack of 27 to 33 individual axial images; Dyn 0 is baseline dynamic acquisition, obtained before contrast agent injection, and Dyn 1 to Dyn 5 are five consecutive dynamic acquisitions obtained after contrast injection. IV, intravenous; TSE, turbo spin echo. Reprinted with permission from: Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Strobel K, et al. J Clin Oncol 2014;32:2304–2310.
