Figure 1.
Reactivation of Cell Pair Co-firing Patterns during POST-Experience Rest Is Already Present at P17, but the Amount of RUN Co-firing Required to Induce Plasticity Is Greater in Young Rats
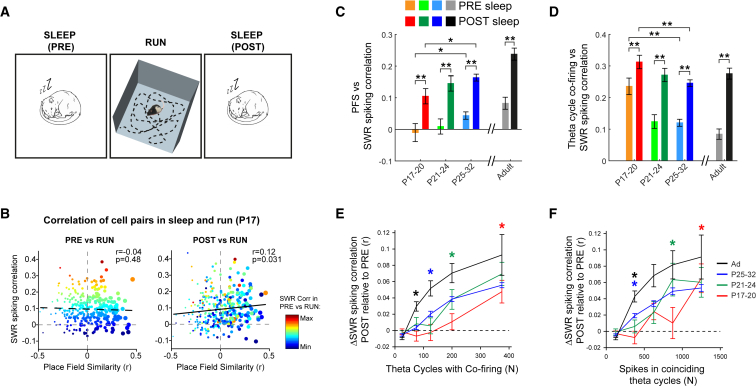
(A) Schematic of experimental paradigm. Rats explored a square open field during RUN and rested in a separate holding box in the same room before (PRE-sleep) and after (POST-sleep) open field exploration.
(B) Example of cell pair co-activity correlation between RUN and temporally adjacent rest sessions in one simultaneously recorded ensemble. Data were recorded at P17 and contain all cell pairs of the ensemble. x axes show place field similarity (PFS) in RUN (Pearson’s r correlation of rate map bin values), y axes correlation of co-firing during SWR events (correlation of cell pair activity across all SWRs in rest) in PRE (left panel) or POST (right panel) rest sessions. Points are colored according to magnitude of SWR spiking correlation in PRE and scaled in size according to their PFS in RUN. Regression statistics are in top right corner. Cell pairs with high PFS show an increase in SWR co-firing during POST-sleep.
(C) Bar chart showing Pearson’s r values (±SE of correlation) of place field similarity (RUN) and SWR spiking correlation for PRE (pale colors) and POST (bold colors) rest sessions for all recorded cell pairs across development. ∗∗ indicates differences at p < 0.001, ∗ differences significant at p < 0.05.
(D) Bar chart showing Pearson’s r values (±SE of correlation) of theta cycle co-firing (RUN) and SWR spiking correlation for PRE (pale colors) and POST (bold colors) rest sessions across development. Asterisks indicate differences at p ≤ 0.001.
(E and F) Cell pair plasticity (change in cell pair SWR spiking correlation from PRE- to POST-sleep) as a function of cell pair co-firing in RUN.
(E) Mean cell pair plasticity (±SEM) as a function of the number of theta cycles in which both cells fire during RUN.
(F) Mean cell pair plasticity (±SEM) as a function of the number of spikes fired in theta cycles in which both cells fire.
For (E) and (F), colored asterisks mark the smallest x axis bin in which cell pair plasticity is significantly different from zero (t test of mean against 0; p < 0.05) at each age.