Figure 1.
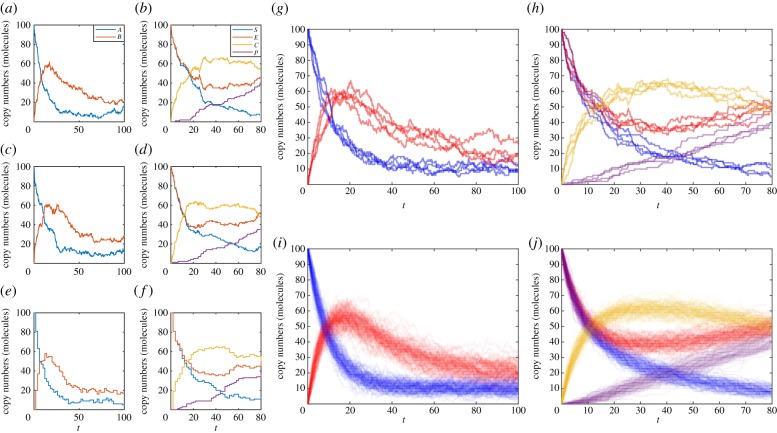
Examples of exact sample paths of the mono-molecular chain model using the (a) Gillespie direct method and (c) modified next reaction method; similarly exact sample paths of the enzyme kinetics model using the (b) Gillespie direct method and (d) modified next reaction method. Approximate sample paths may be computed with less computational burden using the tau-leaping method with τ = 2, at the expense of accuracy: (e) the mono-molecular chain model and (f) the enzyme kinetics model. Every sample path will be different; as demonstrated by four distinct simulations of (g) the mono-molecular chain model and (h) the enzyme kinetics model. However, trends are revealed when 100 simulations are overlaid to reveal states of higher probability density using (i) the mono-molecular chain model and (j) the enzyme kinetics model. The mono-molecular chain model simulations are configured with parameters k1 = 1.0, k2 = 0.1, k3 = 0.05, and initial state A(0) = 100, B(0) = 0. The enzyme kinetics model simulations are configured with parameters k1 = 0.001, k2 = 0.005, k3 = 0.01, and initial state E(0) = 100, S(0) = 100, C(0) = 0, P(0) = 0. (Online version in colour.)