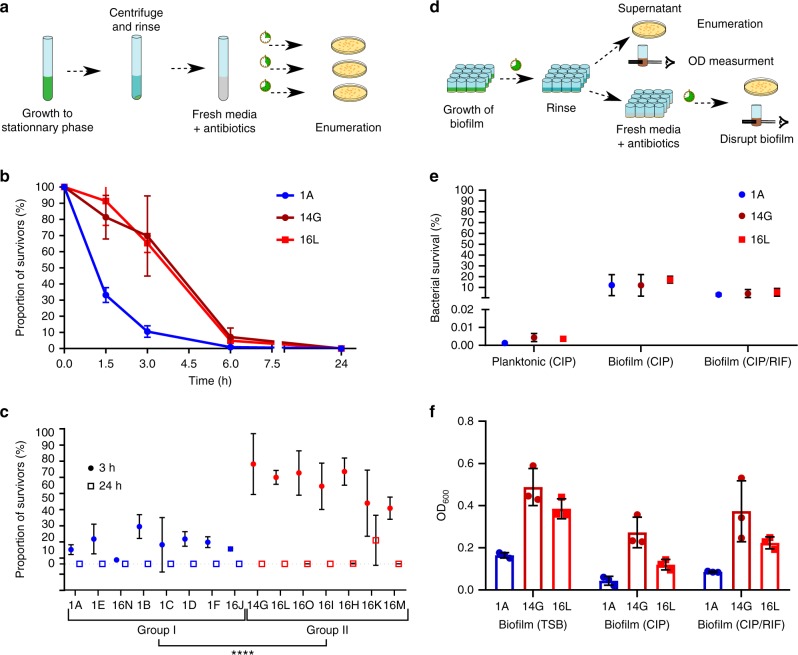
Fig. 6.
Antibiotic clearance of planktonically growing and biofilm-embedded bacteria. a Illustration of the assay used to determine the proportional killing of a bacteria population by antibiotics. b, c Ciprofloxacin killing of stationary growth phase bacteria. Bacteria were exposed to at least 40-fold MIC of ciprofloxacin for b 1.5, 3, 6, and 24 h and for c 3 and 24 h, respectively. The proportion of surviving bacteria relative to the inoculum was quantified by assessing the number of colony-forming units (CFUs) grown on agar plates. Curves and time points show averages of three replicates with standard deviation. Statistical significance of survival to 3 h antibiotic exposure between the two groups was determined by Welch's t test (N = 46 t(30.86) = −10.038, P = 3.069 × 10−11). A log scale representation is given in Supplementary Fig. 6a, b. d Illustration of the assay used to determine the antibiotic treatment efficiency of biofilms. Bacterial killing within a biofilm was measured by enumerating CFUs, and disruption of the biofilm was quantified by optical density after treatment with antibiotics. e Antibiotic killing of bacteria embedded within a biofilm by ciprofloxacin and a combination of ciprofloxacin and rifampicin as compared with stationary phase grown bacteria (same data points as shown in b). The proportion of surviving bacteria relative to the bacteria recovered from the pre-grown biofilm was quantified by assessing the number of CFUs grown on agar plates. Averages with standard deviation of three replicates are shown. A log scale representation is given in Supplementary Fig. 6c. f Quantitative in vitro biofilm assays of untreated, ciprofloxacin, and a combination of ciprofloxacin- and rifampicin-treated biofilm. Biofilms were quantified by OD600 measurement. Averages with standard error of mean of three replicates are shown. Group I and group II isolates are indicated in blue and red, respectively. Dark red indicates the clinical isolate retrieved from the blood culture. ****P < 0.0001