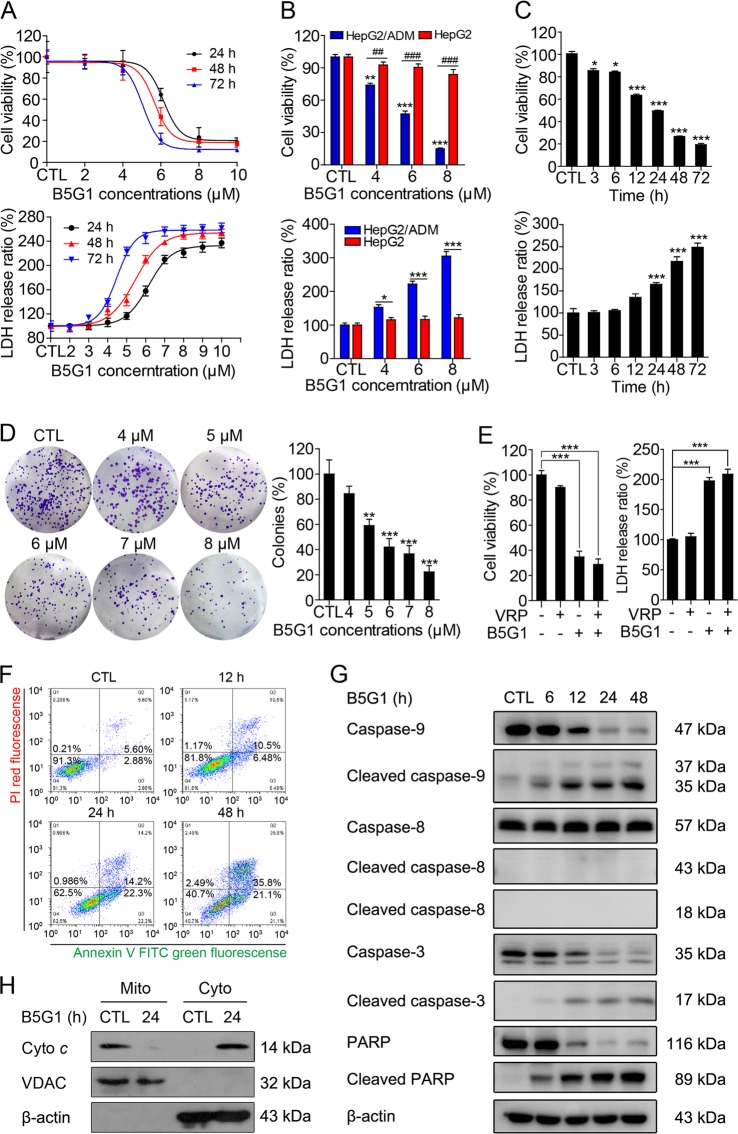
Fig. 1. B5G1 inhibits the proliferation of HepG2/ADM cells via induction of mitochondrial apoptosis.
a HepG2/ADM cells were treated with different concentrations of B5G1 for 24, 48, and 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT and LDH assay. b HepG2/ADM and HepG2 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of B5G1 for 48 h, and cell viability was determined by MTT and LDH assay (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs CTL (HepG2/ADM), ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 (MTT assay); *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (LDH assay). c HepG2/ADM cells were treated with B5G1 (6 μM) for the indicated times, and cell viability was determined by MTT and LDH assay (n = 3). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs CTL. d HepG2/ADM cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of B5G1 for 24 h. Colonies were visualized by crystal violet staining and counted manually (n = 3). Magnification: ×200; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs CTL. e HepG2/ADM cells were treated with B5G1 (6 µM) in the presence or absence of VRP (50 µM) for 48 h, cell viability was measured by MTT and LDH assay (n = 3). ***P < 0.001. f The apoptosis rates of HepG2/ADM cells treated with B5G1 (6 μM) were detected by flow cytometry. g Apoptosis-related proteins expression level of HepG2/ADM cells treated with B5G1 (6 μM) for the indicated times were analyzed by western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. h Cell lysates of HepG2/ADM cells treated with B5G1 (6 μM) for 24 h were divided into cytoplasmic fractions and mitochondrial fractions. Cyto c translocation was measured by western blotting. β-actin and VDAC were used as loading controls for cytoplasm and mitochondria, respectively