Fig. 5.
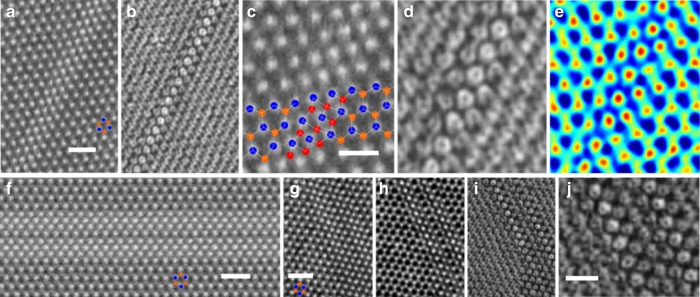
4D STEM of larger width line vacancy channels in WS2. a LAADF image of a 3S line defect in WS2 reconstructed from the 4D STEM data. Scale bar indicates 1 nm and is applicable for panel (b). Blue spots indicate W and orange 2S positions. b |E┴| image reconstructed from 4D STEM data. c Magnified view of the ADF-STEM image reconstructed from 4D STEM data of a 3S line vacancy, S vacancy sites indicated by red dots. Blue dots mark W atom sites and orange dots 2S sites. Scale bar indicates 0.5 nm and is applicable to panels (c)−(e). d |E┴| image reconstructed from 4D STEM data. e Total charge map reconstructed from 4D STEM data. Color scaling is the same as that used in Fig. 2m. f High-resolution ADF-STEM image recorded using an annular detector of a complex wider line defect in WS2. Scale bar indicates 1 nm. Blue spots indicate W atom sites and orange indicates 2S sites. g LAADF image of a complex line defect in WS2 reconstructed from the 4D STEM data. Scale bar indicates 1 nm and is applicable to panels (g)−(i). Blue spots indicate W atom sites and orange indicates 2S positions. h Ptychographic phase of a complex line defect area in WS2 reconstructed using the ePIE algorithm applied to 4D STEM data. i |E┴| map around a complex line defect in WS2 reconstructed from 4D STEM data. j Magnified view of the |E┴| map in (i). Scale bar indicates 0.5 nm