Figure 1.
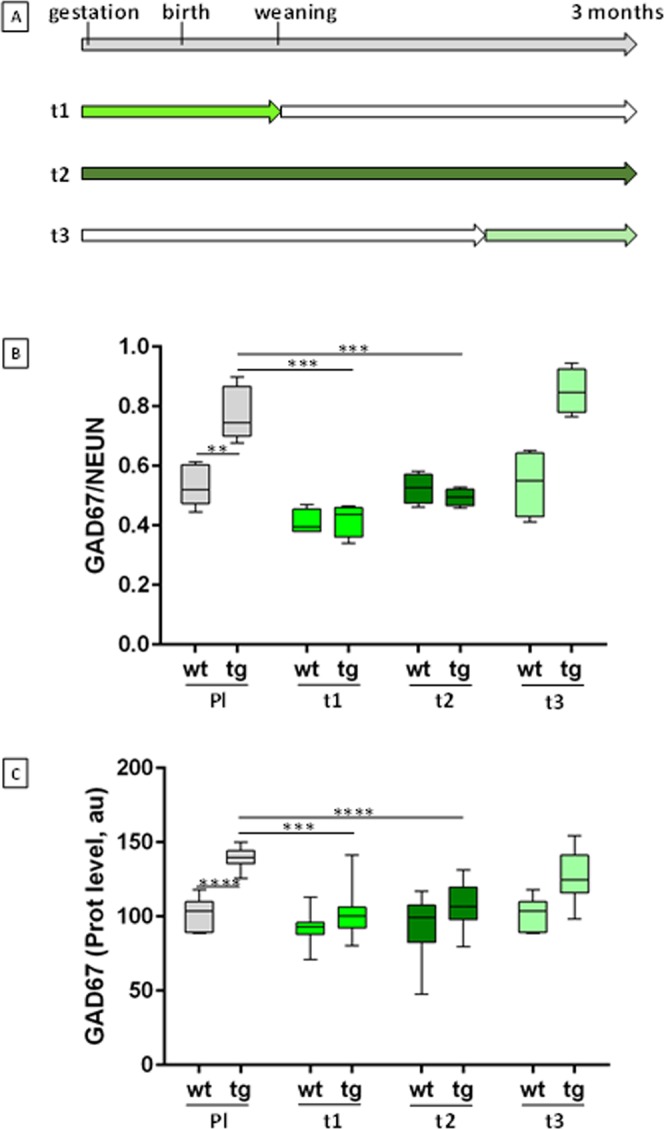
EGCG treatment during brain development of mBACtgDyrk1a mice. (A) Timelines of treatment of mBACtgDyrk1a transgenic (tg) mice from gestation through adulthood with normal food pellets or pellets (SAFE company) containing 600 mg/kg MGTE (decaffeinated Lifeextension extract containing 45% EGCG) and corresponding to a daily dose of 50 mg/kg EGCG for a 25 g mouse. Food consumption was similar for wt and tg animals. T1 treatment started at gestation and continued through weaning. T2 treatment started at gestation and continued until 90 days. T3 treatment started at P60 and continued until P90. Grey indicates standard food (placebo); green indicates treatment on each timeline. (B) Quantification of GAD67+ neuron fraction of NeuN+ neurons in immunohistochemically stained sections of stratum radiatum of control (n = 5) or treated (n = 4) wildtype (WT) and transgenic (TG) mice: serial sagittal brain cryosections (50 µm) were cut on a cryostat and immunohistochemistry was performed with GAD67 (Millipore MAB5406) and NeuN (Millipore ABN 78) antibodies. NeuN-positive and GAD67-positive neuron densities were assessed with StereoInvestigator (MBF) in stratum radiatum in parasagittal slices (+0.36 mm). n = 5 for wt and tg; n = 4 for treated wt and treated tg. (C) Relative GAD67 levels in hippocampus of control or treated WT and TG mice. Arbitrary units (au) of GAD67 levels were normalised to total protein levels and to controls (n = 10). Two ways ANOVA were performed followed by an Holm–Sidak multiple comparison procedure with ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
