Fig. 6.
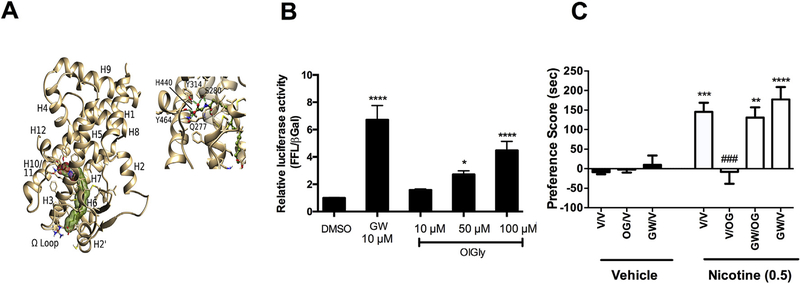
PPAR-α mediates the anti-reward effects of OlGly. (A) Representative frame from MD of OlGly/PPAR-α complex and details of ligand-protein interactions in the ligand binding site. The carboxylic moiety of the ligand recapitulates the main polar stabilizing interactions with Tyr464(H12), Tyr314(H5), His440(H10/11) and Ser280(H3), signature of a PPAR-α agonist. (B) Luciferase Assay for PPAR-α/RXR. Relative Luciferase Units in response to OlGly and the PPAR-α agonist GW7647 (comparison drug). DMSO (n = 12), GW7647 (GW) 10 mM (n = 6), OlGly 10 mM (n = 7), 50 μM (n = 9) and 100 mM (n = 11). ****p < 0.0001, *p < 0.05 vs DMSO (C) The selective PPAR-α antagonist GW6471 (2 mg/kg) prevented OlGly-induced inhibition of nicotine CPP. n = 6–8 mice per group. ****p < 0.0001. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle/vehicle; ###p < 0.001 vs. nicotine/vehicle. Values represent the mean ± SEM.