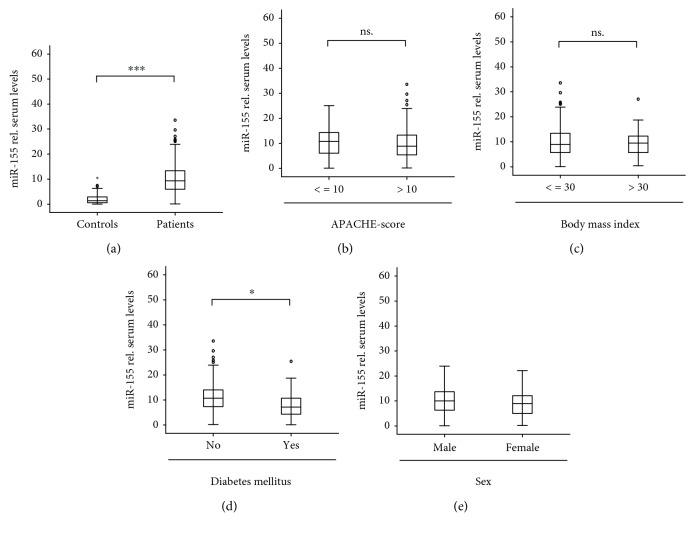
Figure 1.
Serum miR-155 levels of critically ill patients at ICU admission. (a) qPCR was used to determine the concentrations of circulating miR-155 at admission to the ICU. In this analysis, critically ill patients (n = 218) displayed significantly higher serum levels of miR-155 compared to healthy controls (n = 76). (b) Serum miR-155 concentrations were independent on disease severity. (c) Serum concentrations of miR-155 were measured in patients with/without diabetes mellitus type 2. (d) Serum concentrations of miR-155 independent on the presence of obesity. (e) Serum concentrations of miR-155 did not vary with respect to patients' sex. ∗∗∗ p < 0.001.