Fig. 5. PEPDG278D inhibits Ttzm-resistant HER2-BC in vivo.
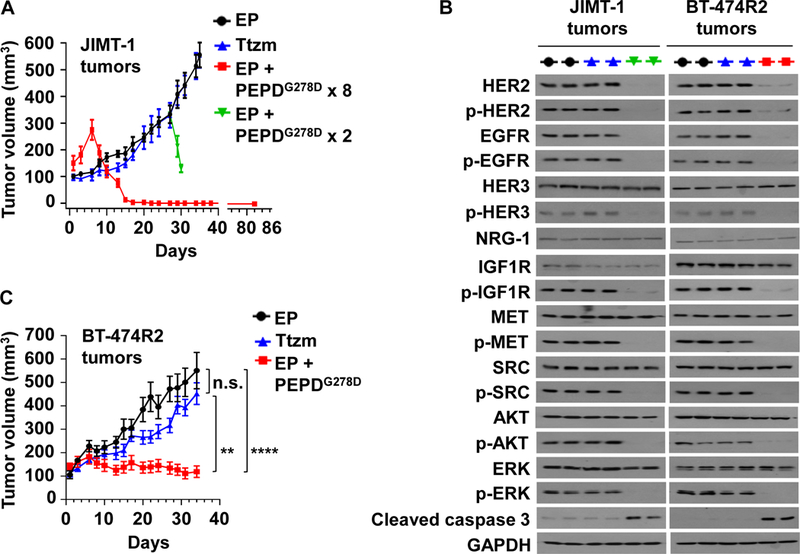
(A) JIMT-1 tumors in SCID mice, treated with EP (daily, days 1–34, n=10), Ttzm (weekly, days 6–34, n=8), or EP + PEPDG278D x 8 (EP daily, days 1–22; PEPDG278D thrice weekly, days 6–22, 8 doses; n=8). In the fourth group, PEPDG278D was added to the EP control on days 27 and 29 (PEPDG278D x 2; n=4). All tumors were harvested 24 hours after the last treatment, but one group of mice (EP + PEPDG278D x 8) became tumor-free and were observed without treatment for 60 days (days 23–82). (B) IB analysis of tumor homogenates (2 tumors/group). See Fig. 1C legend for protein phosphorylation sites. (C) BT-474R2 tumors in nude mice, treated with EP daily (days 1–34, n = 13), Ttzm weekly (days 6–34, n =15), or EP daily (days 1–34) plus PEPDG278D thrice weekly (days 6–34) (n = 12). All tumors were harvested 24 hours after the last treatment. EP, Ttzm and PEPDG278D were dosed ip at 0.5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg and 4 mg/kg per dose, respectively. Each value in (A and C) is mean ± SEM **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test; n.s., not significant.
