Figure 1.
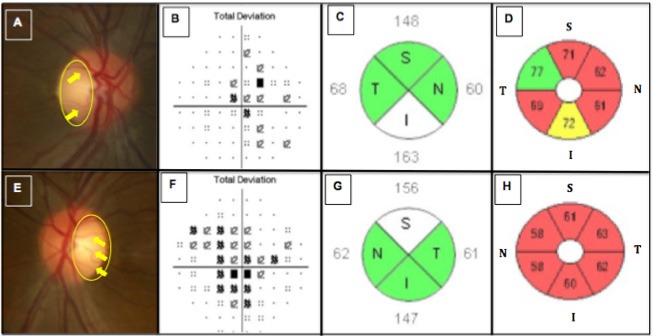
Shows images of the right and left eyes in the LHON patient. Disc photographs (A, E) show temporal pallor (yellow circle) and peripapillary telangiectatic blood vessels along with vascular tortuosity (yellow arrows) for the right (A) and left eyes (E), respectively. Humphrey visual field testing revealed cecocentral scotomomas more severe in the left (F) than in the right eye (B), having mean deviations (MD) of -3.82 and -2.75, respectively. Spectral-Domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) imaging of the peripapillary nerve fiber layer (pRNFL) (C,G) showed relative axonal swelling, most pronounced in the inferior and superior quadrants of the right (C) and left (G) eyes, respectively. SD-OCT imaging of the macular retinal ganglion cell and inner plexiform layers (RGC-IPL) (D,H) revealed diffuse ganglion cell atrophy, more severe in the primarily involved left eye (H) than the secondarily involved right eye (D).
