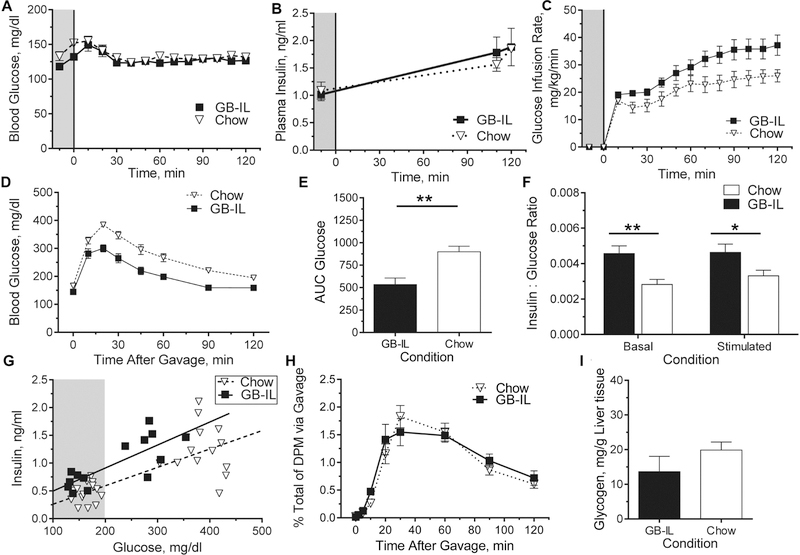
Figure 3. Glucose metabolism in lean, chronic bile diversion mice.
Chronic bile diversion mice underwent clamp studies at 4 weeks postoperative for whole body and tissue-specific assessment of insulin sensitivity and glucose kinetics. (A) Blood glucose was clamped at 5h fasted levels, with a (B) constant insulin infusion to elevate plasma insulin concentrations over food-restricted levels and a (C) variable glucose infusion to maintain euglycemia among the groups. (D) Chow and GB-IL mice also underwent standard oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT; 2 mg/kg body weigh) at 4 weeks postoperatively; and (E) the corresponding area under curve (AUC0–120) glucose was calculated. (F) Ratios of insulin to glucose at baseline (t = 0 min) and following glucose gavage (t = 20 min) were assessed. (G) Regression lines obtained when comparing the glucose and insulin concentrations at basal fasting (shaded gray) and 20 min after glucose stimulation during an OGTT. Slopes among all lines are not significantly different, while the intercept for GB-IL compared to Chow is higher (P<0.01). (H) 3-[3H]-O-methylglucose (3-OMG) counts in peripheral circulation after administering glucose supplemented with 3-OMG tracer during OGTT. (I) Liver glycogen in 5h fasted GB-IL and Chow controls. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. Kruskal-Wallis test of Chow, GB-D (data not shown), GB-IL, adjusted for multiplicity, was used on sample sizes of (A-C) 6 GB-IL, 8 Chow. (D-E) 13 GB-IL, 16 Chow; (F, G) 7 GB-IL, 14 Chow; (H) 6 GB-IL, 7 Chow; (I) 9 GB-IL, 12 Chow. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.