Figure 4. Effects of FGF19 treatment on NPC1L1 expression and cholesterol uptake in intestinal organoids from WT and SHP-knockout mice.
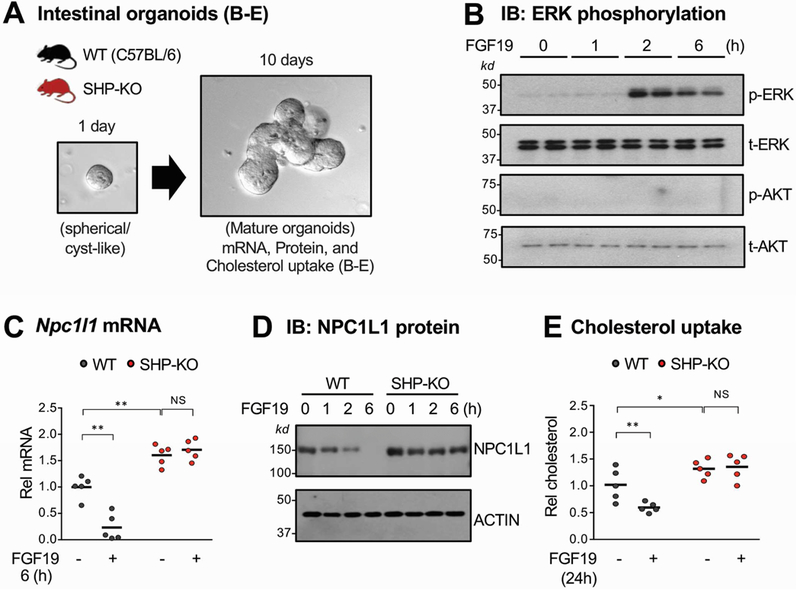
(A) The jejunum and ileum were isolated from WT or SHP-knockout (KO) mice, pooled, and intestinal organoids were cultured and maintained for 10 days as described in Methods. (B-D) Organoids were treated with 50 ng/ml FGF19 for the indicated times. (B) Levels of phosphorylated ERK were determined by IB. (C-D) NPC1L1 mRNA (C) and protein (D) levels were determined by RT-qPCR and IB, respectively. (E) Organoids were cultured in the IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium containing NBD-cholesterol and treated with vehicle or 50 ng/ml FGF19 for 24 h. After washing with PBS, the fluorescence in the cells was determined with excitation at 485 nm and emission at 535 nm as described in Methods. (C, E) Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with the FDR post-test, (SEM, n=5, *P <0.05, **P <0.01, NS, statistically not significant).
