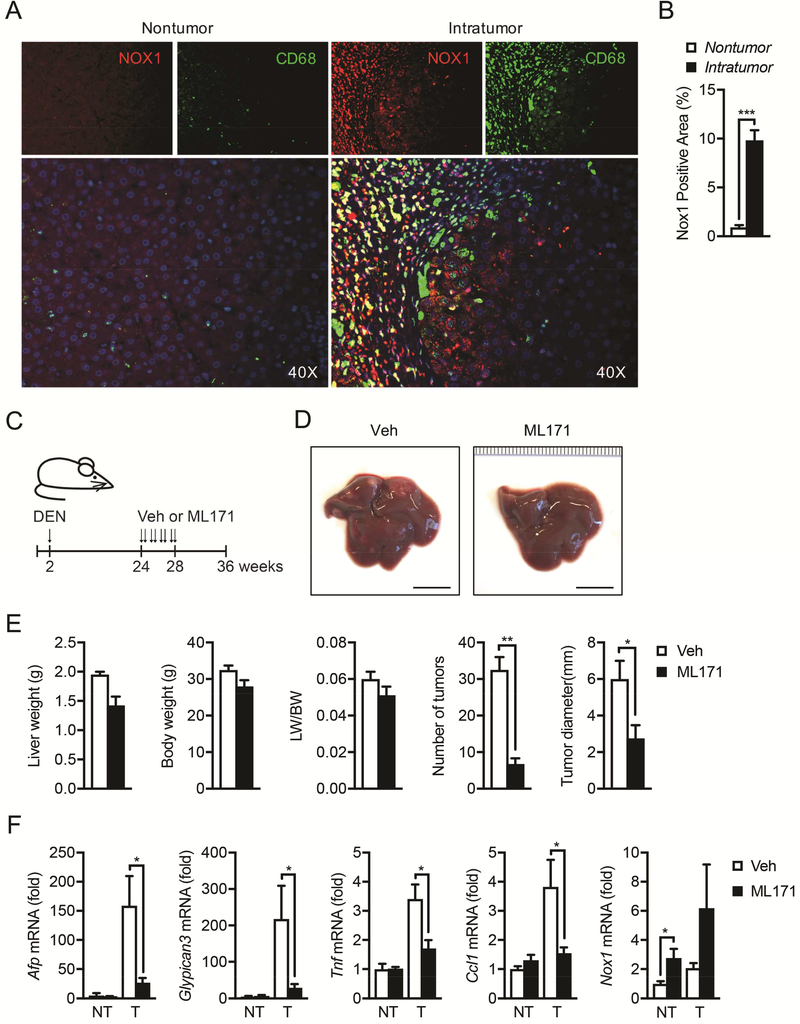
Figure 7. NOX1 is upregulated in tumor-associated macrophages in HCC patients, and NOX1 represents a therapeutic target for HCC.
(A) NOX1 expression in macrophages from paraffin sections of non-tumoral and intratumoral tissue of HCC patients was analyzed by immunofluorescent microscopy. NOX1, red; CD68, green; DAPI, blue. (B) Quantification of positive staining area of NOX1 in non-tumoral (n=7) and intratumoral (n=10) tissue of HCC patients. (C) Schematic representation of DEN induced HCC model and treatment with NOX1 specific inhibitor (ML171). Two-week-old mice were intraperitoneally injected with DEN (25mg/kg), and ML171 (diluted in PBS at 25μM, 100μl per mouse) was administrated via i.p. twice a week for 4 weeks. Mice were sacrificed at 36 weeks old. (D) Representative livers from DEN-injected mice of indicated treatment group 9 month after birth (scale bar, 1cm). (E) Liver weight/body weight (LW/BW) ratios, tumor numbers and maximum sizes of DEN-induced HCCs (n=4 mice/group). (F) Relative expression of Afp, Gpc3, Tnf, Ccl1 and Nox1 in tumor (T) and non-tumor (NT) tissues from indicated mice was quantified by real-time RT-PCR (n=4 mice/group). Results are means ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test for independent samples and unequal variances was used to assess statistical significance (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).