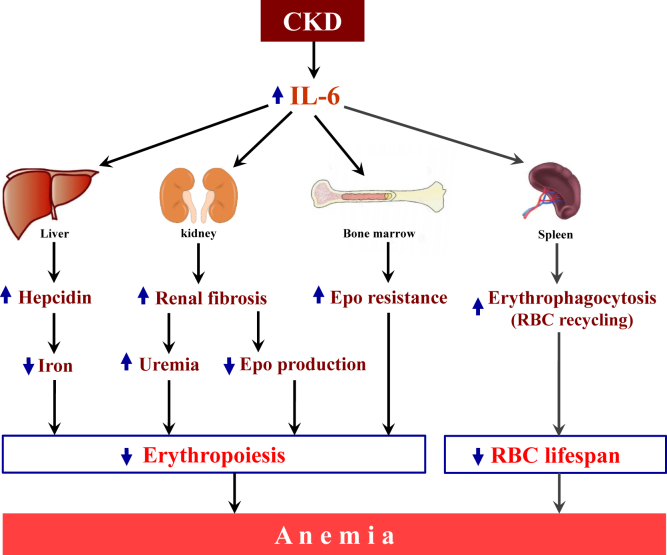
Figure 8.
Proposed model for the role of interleukin (IL)-6 in chronic kidney disease (CKD)–anemia. Increased circulating levels of IL-6 in CKD induce hepcidin overproduction, leading to decreased iron availability for erythropoiesis. In addition, IL-6 appears to aggravate resistance to high levels of circulating erythropoietin (Epo) in early CKD. Furthermore, IL-6 aggravates renal fibrosis, which worsens uremia and reduces the ability of the kidney to produce Epo in advanced CKD. RBC, red blood cell.